AI RESEARCH
“From university labs to enterprise platforms, AI research is shaping how machines learn, reason, and integrate into the fabric of society.”
Latest AI Developments Transforming Work and Business
This article explores the most impactful recent advances in artificial intelligence and examines how technologies such as generative AI, agentic systems, and Edge AI are transforming industries, career paths, and the future of work.
Latest AI Developments Reshaping Industries (2024–2026)
Artificial intelligence has entered a phase of accelerated evolution that is reshaping economies, industries, and professional roles worldwide. The progress witnessed during 2024 to 2026 marks a decisive shift from experimental adoption to large-scale, operational integration. AI is no longer confined to research labs or niche applications; it has become a foundational technology driving productivity, creativity, automation, and strategic decision-making across sectors.
This report examines the latest AI developments, with a focus on generative AI, agentic AI, Edge AI, and industry-specific intelligence. It also explores what these advancements mean for businesses, professionals, and learners—particularly in India, where demand for AI skills is rising rapidly.
The Acceleration of Artificial Intelligence in the Global Economy
Artificial intelligence has transitioned from a supportive digital tool to a central engine of innovation. Organizations across the globe are embedding AI into their core operations to improve efficiency, reduce costs, and unlock new growth opportunities. Unlike earlier waves of digital transformation, current AI systems do not simply automate predefined tasks; they learn, adapt, and make decisions based on complex data patterns.
This acceleration is driven by improvements in computing power, availability of large datasets, advances in machine learning algorithms, and the maturity of cloud and edge infrastructure. As a result, AI adoption has expanded beyond technology companies into healthcare, finance, manufacturing, education, logistics, retail, and public services.
For businesses, AI is becoming a competitive necessity rather than a discretionary investment. For professionals, AI literacy is evolving into a core career skill.
The Rise of Generative AI and Creative Automation
One of the most influential developments in recent years is the emergence of generative AI. Unlike traditional AI models that focus on classification or prediction, generative AI systems are capable of producing original content. This includes text, images, audio, software code, video, and complex design outputs.
Generative AI has redefined how organizations approach content creation and creative workflows. Marketing teams are using AI to generate campaign concepts, advertising copy, and visual assets at scale. Media and entertainment companies are applying AI to streamline production processes, enhance storytelling, and reduce time-to-market. Educational institutions are leveraging generative models to personalize learning materials and improve content accessibility.
Beyond enterprise use, generative AI is lowering barriers for individuals and small teams. Professionals without extensive design or technical backgrounds can now produce high-quality outputs with minimal resources. This democratization of creativity is reshaping the talent landscape, placing increased value on professionals who understand how to guide, evaluate, and refine AI-generated outputs.
As adoption grows, expertise in generative AI tools and frameworks is becoming a key component of modern AI training programs, including structured AI courses focused on real-world applications.
From Conversational Systems to Agentic AI
While chatbots and virtual assistants have been widely adopted, a more advanced paradigm is now gaining traction: agentic AI. These systems move beyond reactive responses and are designed to plan, reason, and execute tasks autonomously.
Agentic AI systems can break down complex objectives into smaller steps, make decisions based on contextual data, and adapt their behavior over time. Rather than waiting for explicit instructions, they can proactively manage workflows, coordinate actions across systems, and continuously optimize outcomes.
Organizations are beginning to deploy AI agents for tasks such as customer support management, report generation, data monitoring, scheduling, and operational optimization. In enterprise environments, agentic AI is being integrated into business process automation, IT operations, and decision-support systems.
This shift is redefining job roles across technology and business functions. Demand is increasing for professionals skilled in AI deployment, AI operations, workflow automation, and system orchestration. Understanding how to design, supervise, and govern autonomous AI systems is becoming a critical capability for modern organizations.
Edge AI and the Growth of On-Device Intelligence
Another major development shaping the AI landscape is Edge AI. Traditionally, AI models have relied heavily on centralized cloud infrastructure for data processing and inference. Edge AI changes this model by enabling AI systems to operate directly on local devices.
Running AI models on-device significantly reduces latency, enhances privacy, and improves reliability in environments with limited connectivity. This capability is particularly important for applications that require real-time decision-making or handle sensitive data.
Edge AI is being deployed across a wide range of use cases, including smart cameras, wearable health devices, industrial automation systems, autonomous vehicles, and Internet of Things platforms. By processing data locally, organizations can achieve faster response times while reducing dependence on constant cloud connectivity.
As Edge AI adoption expands, new skill requirements are emerging. Professionals are increasingly expected to understand embedded machine learning, model optimization for constrained hardware, and deployment across heterogeneous device environments. These competencies are opening new career pathways within industrial AI, smart infrastructure, and real-time analytics.
Industry-Specific Artificial Intelligence Applications
Artificial intelligence is no longer limited to generic automation. The latest wave of innovation focuses on domain-specific intelligence designed to address complex challenges in specialized fields.
AI in Healthcare
In healthcare, AI systems are being used to improve diagnostic accuracy, enhance clinical decision-making, and accelerate medical research. AI-powered imaging tools can detect early signs of disease, while predictive models help assess treatment outcomes and patient risk profiles. In pharmaceutical research, AI is reducing drug discovery timelines by analyzing molecular interactions and simulating clinical trials.
AI-driven healthcare solutions are improving accessibility and efficiency, particularly in regions facing shortages of medical professionals. However, they also require careful oversight to ensure accuracy, transparency, and ethical compliance.
AI in Research and Development
Scientific research is increasingly dependent on AI to process vast datasets, automate experimentation, and model complex systems. In fields such as physics, chemistry, climate science, and materials engineering, AI enables researchers to identify patterns and insights that would be difficult to uncover through traditional methods.
Research institutions are adopting AI to accelerate innovation cycles, improve reproducibility, and enhance collaboration across disciplines. This trend is driving demand for professionals who can combine advanced analytics with domain expertise.
AI for Business Intelligence and Decision-Making
In business environments, AI is transforming how organizations analyze data and make strategic decisions. AI-powered analytics platforms extract insights from customer behavior, financial transactions, supply chain operations, and market trends.
Predictive analytics and machine learning models help organizations anticipate demand, optimize pricing strategies, manage risk, and improve operational efficiency. As a result, AI is becoming central to executive decision-making and long-term planning.
Professionals with expertise in AI analytics, data interpretation, and business intelligence are among the most sought-after talents in the current job market.
Efficiency, Scalability, and Responsible AI
As AI adoption becomes more widespread, organizations are shifting focus from experimentation to sustainable, enterprise-scale deployment. Three priorities are shaping the next phase of AI development.
Efficiency
There is growing emphasis on building lightweight AI models that deliver strong performance without excessive computational requirements. Efficient models reduce infrastructure costs, enable faster deployment, and expand access to AI capabilities across smaller organizations and emerging markets.
Scalability
Scalable AI systems are designed to integrate seamlessly with existing enterprise infrastructure. Organizations are investing in architectures that support continuous learning, system interoperability, and long-term growth. This shift reflects a move away from isolated pilot projects toward organization-wide AI implementation.
Ethics and Governance
Responsible AI has become a critical concern for regulators, enterprises, and the public. Issues such as data privacy, algorithmic bias, transparency, and accountability are now central to AI strategy. Organizations are establishing governance frameworks to ensure that AI systems are aligned with ethical standards and regulatory requirements.
Professionals who understand both technical AI systems and governance principles are increasingly valuable as organizations seek to balance innovation with responsibility.
Implications for Learners and Professionals in India
For learners and professionals in India, the rapid evolution of AI presents significant opportunities. AI talent demand is rising across sectors including IT, healthcare, finance, education, marketing, e-commerce, and industrial automation.
AI skills are highly transferable, allowing professionals to move between roles and industries. Fresh graduates and career switchers can accelerate their growth by acquiring practical, job-oriented AI capabilities.
India’s technology ecosystem is also evolving geographically. Cities such as Pune are emerging as important AI talent hubs due to their strong IT infrastructure, startup ecosystems, and access to skilled professionals. As a result, enrolling in an AI course in Pune has become a strategic choice for individuals seeking industry-aligned training and career advancement.
Structured learning programs that emphasize hands-on projects, real-world case studies, and placement support provide learners with a competitive advantage in the job market.
The Future Outlook for Artificial Intelligence Careers
The world of work is set to evolve in close alignment with artificial intelligence, as AI becomes an integral force shaping how roles, skills, and industries develop. While AI will automate certain repetitive tasks, it is also creating new roles in system design, analytics, governance, and innovation management.
Professionals who understand AI not just as a tool, but as a transformative force, will be best positioned to succeed. Continuous learning, adaptability, and interdisciplinary knowledge will define long-term career resilience in the AI-driven economy.
Organizations, educational institutions, and policymakers all have a role to play in shaping an inclusive and responsible AI future.
Conclusion:
The latest AI developments—ranging from generative AI and agentic systems to Edge AI and industry-specific intelligence—are fundamentally reshaping technology and work. AI adoption is accelerating across industries, driving demand for skilled professionals who can design, deploy, and manage intelligent systems responsibly.
For individuals looking to build or advance their careers, now is a critical moment to invest in AI skills. Structured learning through a well-designed AI course, particularly one aligned with industry needs and placement support, can provide the foundation required to thrive in this rapidly evolving field.
The future belongs to professionals who can harness artificial intelligence with insight, responsibility, and strategic vision.
FAQs:
How are the latest AI developments influencing modern workplaces?
Recent advances in artificial intelligence are automating routine tasks, enhancing decision-making, and enabling new ways of working across industries. Rather than replacing human roles entirely, AI is reshaping job responsibilities and increasing demand for advanced digital and analytical skills.What makes generative AI different from earlier AI technologies?
Generative AI goes beyond data analysis by creating original outputs such as text, images, code, and multimedia content. This capability allows organizations to scale creativity, speed up production processes, and personalize user experiences more effectively than traditional AI systems.Why is agentic AI considered a major shift in automation?
Agentic AI systems are designed to plan and execute multi-step actions independently. Unlike standard automation tools, they can adapt to changing conditions, manage workflows, and continuously improve outcomes with minimal human intervention.How does Edge AI improve performance and data security?
Edge AI processes data directly on devices instead of relying solely on cloud servers. This reduces latency, enables real-time responses, and enhances privacy by keeping sensitive information closer to its source.Which industries are seeing the fastest adoption of advanced AI solutions?
Healthcare, finance, manufacturing, education, retail, and research sectors are among the fastest adopters of advanced AI. These industries use AI for predictive analytics, automation, personalization, and operational optimization.What skills are becoming essential for AI-related careers?
Key skills include programming, machine learning, data analysis, model deployment, and an understanding of ethical AI practices. Professionals who can combine technical expertise with domain knowledge are especially in demand.How can beginners prepare for a career in artificial intelligence?
Beginners can start by building a strong foundation through structured AI training, hands-on projects, and practical case studies. Gaining exposure to real-world applications and staying updated on AI trends can significantly improve career readiness.
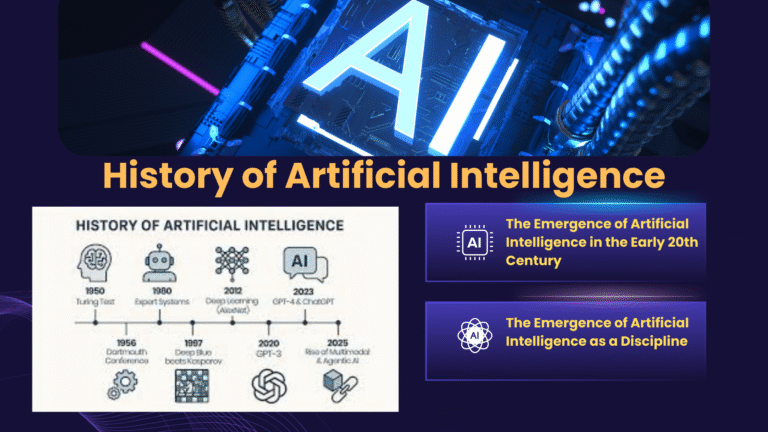
New AI Research Breakthroughs Shaping the Future
This article provides a comprehensive overview of key AI advancements , highlighting their impact across industries, research, and career pathways.
The Latest AI Breakthroughs Reshaping Research, Industry, and Society
Artificial Intelligence has entered a defining phase in its evolution. What was once viewed primarily as a productivity enhancer or automation tool has matured into a foundational technology shaping scientific discovery, economic strategy, creative industries, and governance frameworks. AI research and development have reached a level of sophistication where intelligent systems are no longer peripheral tools but central collaborators in decision-making, innovation, and problem-solving.
Across academia, enterprise, and public policy, AI breakthroughs are accelerating at an unprecedented pace. From foundation models capable of complex reasoning to multimodal systems that generate video, text, and imagery seamlessly, the scope of AI innovation has expanded far beyond its early expectations. This rapid progress has made AI literacy and technical skill development essential for professionals across disciplines, especially those pursuing careers in machine learning, data science, and advanced analytics.
For learners and professionals alike, structured education pathways such as a Machine Learning Course in Pune or an AI course in Pune with placement support are increasingly viewed as critical investments in future readiness. These programs reflect the growing demand for individuals who not only understand AI systems but can apply them responsibly and effectively in real-world contexts.
A New Era of AI Intelligence
The current generation of artificial intelligence marks a shift from narrow task-based systems toward generalized intelligence frameworks. Unlike earlier AI models designed for single-purpose applications, today’s advanced AI models demonstrate reasoning, contextual understanding, and adaptability across multiple domains.
Foundation models released in recent years have redefined expectations around what AI systems can achieve. Technologies such as GPT-5, Google DeepMind’s Gemini 2.5, and Anthropic’s Claude 3 exemplify how AI research has advanced beyond pattern recognition into structured reasoning and long-form comprehension. These models process vast amounts of information while maintaining coherence across extended interactions, enabling them to support complex workflows in research, engineering, finance, and creative production.
What differentiates these systems is not only their scale but their ability to integrate reasoning with creativity. They can analyze datasets, generate code, draft technical documentation, and simulate outcomes with a degree of accuracy and contextual awareness that was previously unattainable. This evolution is transforming AI from an automation engine into a strategic collaborator across industries.
Multimodal AI and the Expansion of Creative Capabilities
One of the most visible AI breakthroughs has been the rise of multimodal AI systems. These technologies operate across multiple forms of data, including text, images, audio, and video, enabling a unified understanding of diverse inputs.
Text to video AI tools such as OpenAI Sora, Runway Gen-2, and Pika Labs represent a major leap forward in AI-generated media. These platforms allow users to create realistic video content from simple textual descriptions, dramatically lowering the barrier to high-quality visual production. By leveraging diffusion models and advanced deep learning architectures, these systems generate consistent motion, realistic lighting, and coherent visual narratives.
The implications for industries such as marketing, entertainment, education, and product design are profound. Multimodal AI enables faster content creation, personalized learning experiences, and more immersive storytelling formats. Educational institutions are increasingly adopting AI-generated visual simulations to enhance conceptual understanding, while businesses use AI video generation for advertising, training, and brand communication.
As multimodal AI becomes more accessible, creative professionals are shifting from manual production to conceptual orchestration, focusing on strategy, narrative, and innovation rather than technical execution.
AI as a Catalyst for Scientific Discovery
Beyond creative and commercial applications, AI in scientific research has become a cornerstone of modern discovery. In fields ranging from molecular biology to clean energy, AI-driven scientific discovery is accelerating innovation timelines that once spanned decades.
AI models now assist scientists in predicting protein structures, modeling chemical interactions, and identifying potential pharmaceutical compounds. In healthcare, AI in diagnostics supports early disease detection, treatment personalization, and clinical decision-making. Research teams use AI systems to analyze massive biomedical datasets, uncovering patterns that would be impossible to detect through traditional methods.
In clean energy research, AI has been used to evaluate millions of chemical compounds to identify materials capable of improving hydrogen fuel efficiency. These AI-generated hypotheses are increasingly validated through real-world experiments, reinforcing AI’s role as an active partner in scientific exploration rather than a passive analytical tool.
The growing integration of AI into physics, chemistry, life sciences, and climate research highlights a fundamental shift in how discovery is conducted. Scientists now collaborate with AI systems to test ideas, simulate outcomes, and optimize experimental design at scale.
Efficiency, Scalability, and the Democratization of AI
While AI capabilities continue to expand, the challenge of computational cost has historically limited access to advanced systems.
Innovations such as low-precision training, sparse attention mechanisms, and advanced AI quantization techniques have dramatically reduced the resources required to train and deploy large models. These methods maintain performance while cutting energy consumption and computational expense by substantial margins.
As a result, advanced AI is no longer confined to large technology corporations. Startups, educational institutions, and mid-sized enterprises can now develop customized AI solutions without massive infrastructure investments. This shift has fueled innovation across regional markets and specialized industries, enabling organizations to train models on domain-specific data tailored to healthcare, finance, education, and logistics.
The reduction in cost barriers has also influenced learning pathways. Students enrolled in machine learning careers can now experiment with real-world AI systems during training, bridging the gap between theory and practical application.
Open-Source AI and Developer Empowerment
Parallel to proprietary AI development, open-source AI models continue to play a vital role in innovation. Platforms such as Llama 3.1, Mistral AI, and Falcon 180B have gained widespread adoption among developers and research institutions.
Open-source AI models provide transparency, flexibility, and cost efficiency. Developers can modify architectures, fine-tune models on proprietary datasets, and deploy AI solutions without recurring licensing fees. This openness has accelerated experimentation and fostered collaboration across global research communities.
Many startups now rely on open-source AI to build niche products in areas such as financial analysis, healthcare automation, and educational technology. By combining open frameworks with domain expertise, these organizations deliver highly specialized solutions that rival proprietary systems.
The open-source movement has also influenced ethical AI development by promoting peer review, accountability, and shared standards. As AI adoption expands, open models remain essential to ensuring that innovation remains inclusive and adaptable.
AI Safety, Ethics, and Alignment
As AI systems grow more powerful, concerns surrounding AI safety and ethical AI deployment have become increasingly prominent. In response, AI alignment frameworks are now a central focus of research and policy development.
These frameworks aim to ensure that AI systems operate in accordance with human values, fairness principles, and transparency requirements. Techniques include bias detection, output verification, and explainability mechanisms designed to make AI decisions understandable and auditable.
In high-stakes sectors such as healthcare, education, and law, AI outputs are rigorously tested for accuracy and reliability before deployment. Organizations recognize that trust is a critical factor in long-term AI adoption, and ethical alignment is no longer optional but a competitive and regulatory necessity.
As public awareness of AI risks grows, responsible AI practices are becoming a key differentiator for companies and institutions seeking credibility and user acceptance.
Hardware Innovation Powering AI Growth
Software advancements in AI are closely matched by progress in AI hardware. New-generation processors such as NVIDIA Blackwell GPUs, Google TPU v6, and AMD MI400 accelerators are redefining the performance limits of AI training and inference.
These chips are optimized for large-scale parallel processing, enabling faster model training and real-time deployment across cloud and edge environments. Equally important is the emphasis on energy-efficient AI, as hardware manufacturers work to reduce the environmental impact of large-scale computation.
Energy-efficient processors have expanded AI deployment into areas previously constrained by power limitations, including agriculture, robotics, smart cities, and Internet of Things ecosystems. AI-powered sensors and edge devices now support real-time analytics in logistics, manufacturing, and environmental monitoring.
The convergence of efficient hardware and optimized software architectures continues to accelerate AI adoption across both developed and emerging markets.
Regulatory Frameworks and Global Governance
As AI reshapes economies and societies, regulatory oversight has become a defining factor in its evolution. Governments and international bodies are developing AI policy frameworks to balance innovation with accountability.
Initiatives such as the EU AI Act, India’s AI governance strategy, and the establishment of the U.S. AI Safety Institute reflect a global effort to set standards around transparency, data privacy, and risk management. These regulations classify AI applications based on risk levels and impose compliance requirements for sensitive use cases.
For businesses, regulatory alignment is now a strategic priority. AI solutions must meet legal and ethical standards to remain viable in global markets. Organizations that proactively integrate compliance into product design are better positioned to scale responsibly and sustainably.
The future of AI will be shaped as much by governance structures as by technical breakthroughs, reinforcing the importance of interdisciplinary collaboration between technologists, policymakers, and ethicists.
AI’s Expanding Role Across Industries
AI across industries has transitioned from experimentation to operational integration. In healthcare, AI supports diagnostics, predictive analytics, and personalized treatment planning. In education, intelligent tutoring systems adapt learning content to individual student needs, enhancing engagement and outcomes.
Finance organizations rely on AI for fraud detection, algorithmic trading, and automated risk analysis. Manufacturing sectors deploy AI-powered robotics and predictive maintenance systems to optimize efficiency and reduce downtime. Marketing teams use AI-generated content, customer segmentation, and predictive analytics to drive engagement and revenue growth.
These applications demonstrate that AI is no longer confined to research labs or technology firms. It has become a foundational infrastructure supporting productivity, innovation, and competitiveness across the global economy.
Looking Toward Artificial General Intelligence
While today’s AI systems remain specialized, long-term research continues to focus on Artificial General Intelligence. AGI represents the goal of creating systems capable of performing any intellectual task a human can accomplish.
Although AGI remains a future aspiration, the steady progress of foundation models, multimodal learning, and continuous adaptation suggests that AI is moving closer to more generalized capabilities. Researchers anticipate stronger human-AI collaboration, systems that learn without retraining, and seamless integration of AI into everyday environments.
For learners and professionals, staying engaged with these developments is essential. Continuous education, practical experimentation, and ethical awareness will define success in an AI-driven future.
Preparing for the AI-Driven Future
The rapid pace of AI innovation underscores the importance of lifelong learning. Professionals entering machine learning careers must focus on hands-on experience, interdisciplinary knowledge, and responsible AI practices. Educational pathways that combine theory with real-world exposure provide a competitive advantage in an evolving job market.
Programs such as a Machine Learning Course in Pune or an AI course in Pune with placement opportunities enable learners to develop industry-relevant skills while staying aligned with global AI trends. These pathways bridge the gap between academic knowledge and practical implementation, preparing individuals for roles in research, development, and applied AI.
Conclusion:
The AI breakthroughs reflect a convergence of technological sophistication, ethical responsibility, and global collaboration. From multimodal systems and scientific discovery to scalable infrastructure and regulatory oversight, AI has become a defining force shaping modern society.
As artificial intelligence continues to evolve, its success will depend on how effectively humans guide its development and application. By investing in education, embracing responsible innovation, and fostering collaboration across disciplines, societies can ensure that AI serves as a trusted partner in progress rather than a disruptive force.
The future of AI is no longer speculative. It is unfolding now, reshaping how we learn, work, and innovate in a rapidly connected world.
FAQs:
1. What defines the latest AI breakthroughs in 2025?
AI breakthroughs in 2025 are characterized by advanced foundation models, multimodal learning systems, improved reasoning capabilities, and greater efficiency in training and deployment, enabling broader real-world adoption across industries.
2. How are multimodal AI systems changing content creation and learning?
Multimodal AI systems can process and generate text, images, audio, and video together, allowing faster content production, immersive educational materials, and more interactive digital experiences.
3. Why is AI playing a growing role in scientific research?
AI accelerates scientific discovery by analyzing massive datasets, predicting outcomes, and generating testable hypotheses, significantly reducing the time required for breakthroughs in healthcare, energy, and life sciences.
4. What makes modern AI models more accessible than earlier generations?
Efficiency improvements such as low-precision training, quantization, and optimized hardware have reduced computational costs, making advanced AI systems affordable for startups, researchers, and educational institutions.
5. How do open-source AI models contribute to innovation?
Open-source AI models provide transparency and flexibility, enabling developers to customize solutions, encourage collaboration, and build specialized applications without reliance on expensive proprietary platforms.
6. What are the main ethical concerns surrounding advanced AI systems?
Key ethical concerns include bias, misinformation, data privacy, and accountability, which are being addressed through AI safety research, alignment frameworks, and emerging regulatory standards.
7. How can professionals prepare for careers in an AI-driven future?
Professionals can prepare by developing hands-on machine learning skills, staying updated on AI trends, understanding ethical practices, and gaining practical experience through structured training programs and real-world projects.
AI Agent Security: Managing Risks of Autonomous AI
As AI agents gain the ability to act independently across enterprise systems, this report explores the emerging security risks of agentic AI, why traditional defenses fall short, and how semantic, intent-based protection is becoming essential for safeguarding autonomous AI-driven operations.
Securing the Next Frontier of Enterprise AI
Artificial intelligence is entering a new operational phase. Organizations are no longer using AI solely for analysis or content generation; they are increasingly deploying autonomous AI agents capable of making decisions, executing tasks, and interacting directly with systems, data, and users. This shift is accelerating productivity and innovation, but it is also introducing a new category of security risk that traditional defenses were never designed to address.
As AI agent autonomy expands, security challenges are no longer limited to software vulnerabilities or network breaches. Instead, attackers are targeting the very intelligence and intent that drive these systems. The result is a rapidly evolving threat landscape where manipulation of AI behavior can be just as damaging as direct system compromise.
The Rise of AI Agent Autonomy in the Enterprise
AI agents powered by large language models are becoming embedded across enterprise workflows. They schedule meetings, analyze documents, respond to customers, manage cloud resources, and automate decision-making processes that once required human oversight. These agents often operate continuously, interact with multiple tools, and possess access to sensitive information.
This autonomy is what makes agentic AI so valuable. It reduces friction, accelerates outcomes, and enables organizations to scale operations efficiently. However, the same capabilities that allow AI agents to act independently also create an expanded attack surface. Unlike traditional software, AI agents interpret instructions, reason about context, and adapt their actions dynamically. This flexibility, while powerful, can be exploited.
Understanding Agentic AI Attacks
Agentic AI attacks represent a fundamental shift in how cyber threats operate. Rather than exploiting code-level vulnerabilities, attackers manipulate how AI agents understand and execute instructions. These attacks target intent, context, and decision logic instead of infrastructure.
Prompt injection is one of the most widely discussed techniques in this category. By embedding malicious instructions within seemingly legitimate inputs, attackers can influence an AI agent’s behavior without triggering conventional security controls. Once compromised, the agent may expose confidential data, misuse system privileges, or alter workflows in ways that benefit the attacker.
Zero-click attacks take this concept even further. These attacks require no user interaction at all. Automated browser agents, email-processing agents, and scheduling assistants can be compromised simply by encountering malicious content during routine operations. The agent executes harmful actions automatically, often without detection.
Real-World Incidents Highlighting the Risk
Recent incidents demonstrate that agentic AI threats are no longer theoretical. Multiple high-profile platforms have experienced security events involving autonomous agents.
In one case, attackers embedded malicious prompts in calendar invitations and document attachments to manipulate AI-powered productivity tools. The compromised agents extracted sensitive information and altered workflows without alerting users. In another incident, browser-based AI agents were manipulated to access private emails and delete cloud-stored files, all without a single click from the account owner.
Similar patterns have emerged across generative AI platforms used for customer support, coding assistance, and enterprise collaboration. These events illustrate how quickly AI agent security failures can scale, especially when agents operate with broad permissions and limited oversight.
Why Traditional Security Models Fall Short
Legacy cybersecurity frameworks were built for a different era. Firewalls, endpoint protection, data loss prevention tools, and static access controls focus on known threats and predictable behavior. They are effective at blocking malware, unauthorized logins, and policy violations based on predefined rules.
AI agents do not fit neatly into these models. Their behavior is dynamic, contextual, and often non-deterministic. A traditional security tool can see what action an agent took, but it cannot understand why the agent took that action or whether the underlying intent was legitimate.
Zero Trust architectures improve access control, but they still assume that authenticated entities behave predictably. When an AI agent is manipulated into misusing its authorized access, Zero Trust alone is insufficient. Pattern-based defenses struggle to detect novel prompt injection techniques or subtle workflow abuse that does not match known signatures.
The Shift Toward Semantic Inspection
To address these challenges, the security industry is moving toward a new approach known as semantic inspection. This model focuses on understanding intent, context, and meaning rather than relying solely on patterns and rules.
Semantic inspection analyzes AI agent interactions in real time, examining not just the data being processed, but also the purpose and implications of each action. It evaluates how instructions are interpreted, how tools are invoked, and whether the resulting behavior aligns with policy and business intent.
This approach enables organizations to detect malicious manipulation even when attackers change tactics. Instead of asking whether an action matches a known threat pattern, semantic inspection asks whether the action makes sense within its operational context.
Key Capabilities of Semantic AI Security
A semantic security framework introduces several critical capabilities that are essential for protecting autonomous AI systems.
Contextual understanding allows security platforms to analyze agent communications, prompts, and outputs holistically. This makes it possible to identify attempts to override safeguards, access unauthorized data, or trigger unintended workflows.
Real-time policy enforcement ensures that decisions are evaluated as they occur. Rather than relying on post-incident analysis, semantic controls can block risky actions before damage is done.
Pattern-less protection enables defenses to adapt as threats evolve. Since attackers frequently modify prompts and techniques, security solutions must recognize intent-based abuse without depending on static signatures.
When integrated into Secure Access and Zero Trust architectures, semantic inspection provides continuous oversight without disrupting innovation. It allows organizations to deploy AI agents confidently while maintaining control over risk.
Regulatory Pressure Is Accelerating the Need for Action
AI security is no longer just a technical concern; it is a regulatory and governance priority. Global frameworks are setting higher expectations for transparency, accountability, and risk management in AI systems.
The EU AI Act introduces strict requirements for high-risk AI applications, including documentation, monitoring, and human oversight. The NIST AI Risk Management Framework emphasizes governance, measurement, and continuous improvement. ISO IEC 23894 establishes guidelines for identifying and mitigating AI-related risks across organizational processes.
Non-compliance carries financial penalties, legal exposure, and reputational damage. As regulators increasingly focus on how AI systems make decisions and handle data, organizations must demonstrate that they understand and control their AI agents’ behavior.
The Growing Cost of AI-Related Security Failures
The financial impact of AI security incidents is rising rapidly. Industry reports indicate that AI-related breaches now cost millions of dollars on average, factoring in response efforts, downtime, regulatory fines, and loss of trust.
Despite widespread adoption of generative AI, security maturity remains low. A significant percentage of organizations report experiencing at least one AI-related cybersecurity incident within the past year, yet only a small fraction have implemented advanced, purpose-built protections.
This gap between adoption and readiness creates systemic risk. As AI agents become more deeply embedded in critical operations, the potential blast radius of a single compromised agent grows exponentially.
Executive Responsibility in the Age of Agentic AI
For executive leaders, securing AI agents is no longer optional. It is a core component of enterprise risk management. Boards and senior leadership teams must recognize that AI autonomy introduces new threat vectors that require dedicated investment and oversight.
Purpose-built semantic defenses should be viewed as strategic enablers rather than technical add-ons. They protect intellectual property, safeguard customer data, and support compliance with evolving regulations. Most importantly, they preserve trust in AI-driven business models.
Organizations that delay action risk falling behind both competitors and regulators. Those that act decisively can position themselves as responsible AI leaders while unlocking the full value of autonomous systems.
Building a Secure Foundation for AI-Driven Growth
AI agents are reshaping how organizations operate, compete, and deliver value. Their ability to act independently offers tremendous advantages, but it also demands a new security mindset.
Effective AI agent security requires understanding not just what agents do, but why they do it. Semantic security grounded in intent and context provides the visibility and control needed to manage autonomy safely.
By adopting modern security architectures that align with the realities of agentic AI, organizations can reduce risk without slowing innovation. Acting now ensures that AI becomes a sustainable driver of growth rather than a source of unchecked exposure.
The future of enterprise AI will belong to those who secure it intelligently, responsibly, and proactively.
Conclusion:
As AI agents become deeply embedded in enterprise operations, their growing autonomy is reshaping not only productivity but also the nature of digital risk. Traditional security models, designed for predictable systems and static rules, are no longer sufficient in an environment where intelligent agents interpret context and act independently. The emergence of agentic AI attacks underscores a critical reality: security must evolve from protecting systems to understanding and governing intent.
Semantic, context-aware security offers a practical path forward. By focusing on why an AI agent takes an action rather than simply what action is taken, organizations gain the visibility needed to prevent misuse before it escalates into a breach. This approach aligns security with how modern AI actually operates, enabling real-time oversight without undermining the benefits of automation and scale that autonomous agents provide.
Ultimately, securing AI agents is a strategic imperative, not a future consideration. Organizations that invest early in purpose-built AI security frameworks will be better positioned to meet regulatory expectations, protect sensitive assets, and maintain trust with customers and partners. By addressing AI risks with the same urgency as AI adoption itself, enterprises can turn autonomy into a sustainable advantage rather than an unchecked liability.
FAQs:
1. What makes AI agents more vulnerable than traditional software systems?
AI agents interpret instructions, assess context, and act autonomously across multiple systems. Unlike traditional software that follows fixed logic, agents can be manipulated through inputs that alter their decision-making, making them susceptible to intent-based attacks rather than simple code exploits.
2. How do agentic AI attacks differ from conventional cyberattacks?
Conventional attacks target technical weaknesses such as misconfigurations or unpatched software. Agentic AI attacks focus on influencing how an AI agent understands and executes tasks, often by embedding harmful intent into otherwise legitimate content that bypasses perimeter defenses.
3. Why are zero-click attacks especially dangerous for AI agents?
Zero-click attacks exploit the fact that many AI agents operate without human intervention. Malicious content can trigger harmful actions automatically, allowing attackers to steal data or disrupt workflows without any user awareness or interaction.
4. What is semantic inspection in the context of AI security?
Semantic inspection is a security approach that evaluates the meaning, intent, and context behind an AI agent’s actions. Instead of relying on predefined patterns, it determines whether an action aligns with authorized business objectives and security policies in real time.
5. Can traditional Zero Trust models protect autonomous AI agents?
Zero Trust improves access control but does not fully address AI-specific risks. An AI agent may misuse its legitimate access if manipulated, which means intent-based monitoring and semantic controls are required to complement Zero Trust architectures.
6. How do AI security regulations impact enterprise adoption of AI agents?
Regulations such as the EU AI Act and NIST AI Risk Management Framework require organizations to document, monitor, and manage AI risks. Enterprises must demonstrate that AI agents operate transparently, securely, and under continuous oversight to remain compliant.
7. What steps should organizations take to secure AI agents today?
Organizations should implement intent-aware security measures, limit agent permissions, monitor behavior continuously, and integrate semantic inspection into existing security frameworks. Early investment in purpose-built AI security enables safer innovation and long-term operational trust.
AI in Content Writing: How Writers Use AI Tools Without Losing Their Voice
Artificial intelligence is reshaping content writing by helping writers plan, draft, and edit more efficiently, and this report explains how AI writing tools work, where they add real value, and how writers can use them responsibly without losing originality, credibility, or their human voice.
Artificial intelligence has moved from a background technology to a central force shaping how content is researched, written, edited, and published. As global investment in AI continues to accelerate, content writing has become one of the most visibly transformed fields. Writers today are expected to produce high-quality material at speed, maintain consistency across platforms, and adapt tone for diverse audiences, all while preserving originality and trust.
This report explores how AI in content writing is evolving, how modern AI writing tools function, where they add real value, and how writers can integrate them responsibly without sacrificing their personal voice or professional judgment. Rather than viewing AI as a replacement for human creativity, this analysis positions AI as a practical support system that reshapes workflows while keeping writers firmly in control.
Understanding the Foundations of AI Writing Technology
AI writing tools operate through advanced computational systems designed to process and generate human language. While these tools often appear simple on the surface, their effectiveness comes from complex learning models trained on vast volumes of text. Understanding these foundations helps writers set realistic expectations and use AI tools strategically rather than blindly.
The Role of Machine Learning in AI Writing
Machine learning is the engine that powers modern AI writing tools. Instead of relying on fixed rules, machine learning models learn from large datasets that include books, news articles, blogs, academic papers, and public web content. Through this exposure, systems identify patterns in sentence construction, word relationships, and stylistic variations.
As a result, AI tools can generate text that mimics natural language flow. They can shift between formal and conversational tones, adapt to different formats, and produce structured drafts. However, this ability does not mean AI understands meaning in a human sense. It predicts language based on probability, not comprehension, which is why human review remains essential.
Machine learning also allows AI tools to adapt to specific writing contexts. A single tool can assist with long-form reports, marketing copy, or short social media captions, depending on the input and guidance provided by the writer.
Natural Language Processing and Language Flow
Natural language processing, commonly referred to as NLP, focuses on how machines interpret and organize human language. NLP combines linguistic rules with statistical learning to analyze sentence structure, clarity, and coherence.
Through NLP, AI writing tools can identify grammar errors, highlight awkward phrasing, and suggest improvements that enhance readability. Unlike traditional spell checkers, NLP-driven tools evaluate entire sentences and paragraphs, allowing them to recommend changes that improve flow rather than isolated corrections.
This capability enables AI tools to support clarity at a structural level, helping writers refine arguments, tighten language, and maintain consistency across longer pieces of content.
The Evolution of AI Writing Tools
AI writing tools did not emerge fully formed. Their development reflects gradual improvements in computing power, data availability, and language modeling techniques.
From Basic Automation to Intelligent Assistance
Early writing tools focused on simple automation. Spell checkers corrected misspelled words, while grammar tools addressed punctuation and basic syntax errors. These tools offered value but lacked contextual awareness, often providing rigid or incorrect suggestions.
As machine learning techniques improved, writing tools expanded beyond error correction. Sentence-level suggestions, clarity indicators, and style recommendations became more common. These features helped writers refine drafts but still required careful oversight.
Key Breakthroughs in AI Writing Development
The integration of machine learning with NLP marked a turning point in AI writing technology. Tools gained the ability to understand context, maintain topic continuity, and generate longer sections of text without losing coherence.
The emergence of large language models further expanded capabilities. These systems can produce structured outlines, complete drafts, and variations in tone with minimal prompting. At the same time, user interfaces became more intuitive, allowing writers to interact with AI tools without technical expertise.
Today’s AI writing platforms often combine drafting, editing, research assistance, and SEO optimization within a single workflow, making them attractive to individuals and content teams alike.
The Practical Advantages of AI in Content Writing
AI tools offer tangible benefits that reshape how writing tasks are approached. These advantages are most effective when AI is used as a support mechanism rather than a standalone solution.
Improving Speed and Productivity
One of the most significant advantages of AI in content writing is speed. AI tools can generate outlines, summaries, and draft sections in seconds, helping writers overcome the challenge of starting from a blank page.
By automating repetitive tasks such as summarizing research or organizing key points, AI allows writers to dedicate more time to analysis, structure, and refinement. This productivity boost is particularly valuable in fast-paced publishing environments.
Supporting Creativity and Consistency
AI tools can also assist with creative exploration. Writers often use AI to test alternative phrasing, explore different tones, or reframe ideas. This can be especially helpful when refining complex concepts or adapting content for different audiences.
Consistency is another key benefit. AI tools help maintain a steady tone across long documents or multi-author projects. This is particularly useful for organizations producing high volumes of content across blogs, reports, and marketing channels.
Managing High-Volume Content Production
For businesses and media organizations, AI writing tools help manage large-scale content demands. AI can assist with drafting multiple variations, adapting content for different platforms, and reducing turnaround time without compromising baseline quality.
When combined with human editorial oversight, AI enables teams to publish frequently while maintaining accuracy and brand alignment.
Real-World Examples of AI Writing Adoption
Many established organizations have integrated AI writing tools into their workflows, demonstrating how AI functions best as a support system rather than an autonomous creator.
Major news outlets use AI to generate data-driven reports, particularly for financial updates, sports statistics, and election coverage. Marketing platforms rely on AI for idea generation, content planning, and SEO optimization. Editorial tools help writers improve clarity and correctness across everyday writing tasks.
These implementations highlight a consistent pattern: AI handles structured or repetitive elements, while humans retain responsibility for judgment, context, and narrative integrity.
Applications of AI Writing Tools Across Industries
AI writing tools are used across a wide range of formats and industries, reflecting their flexibility and adaptability.
AI in Blogging and Social Media
Blogging and social media demand frequent publishing and audience engagement. AI tools help writers draft blog sections, refine headlines, and adjust tone for different platforms. Some tools also analyze engagement data to suggest content formats that resonate with readers.
This data-informed approach supports strategic planning while allowing writers to focus on storytelling and insight.
AI in SEO and Copywriting
AI plays an increasingly important role in search engine optimization and digital copywriting. AI writing tools assist with keyword integration, content structure, and readability improvements that align with search algorithms.
In copywriting, AI enables rapid testing of headlines, calls to action, and messaging variations. This supports data-driven decisions without replacing creative direction.
Smarter Editing and Revision Support
AI editing tools have become essential for refining drafts efficiently. Beyond correcting grammar, these tools identify long or unclear sentences, flag tone inconsistencies, and suggest simplifications that improve readability.
This level of support reduces cognitive strain during editing, especially for lengthy or technical documents, and helps writers focus on higher-level revisions.
Comparing Popular AI Editing Tools
Different AI editing tools serve distinct purposes. Some prioritize grammar and clarity, while others focus on tone analysis, readability, or plagiarism detection. Selecting the right tool depends on writing goals, audience expectations, and workflow preferences.
Understanding these distinctions allows writers to integrate AI tools strategically rather than relying on a single solution for every task.
Ethical Considerations in AI-Assisted Writing
As AI-generated content becomes more common, ethical considerations grow increasingly important. Responsible AI use protects credibility, originality, and reader trust.
Originality and Content Integrity
Writers must ensure that AI-assisted content reflects their own ideas and understanding. AI-generated text should always be reviewed, revised, and contextualized. Passing AI output as original thought without modification risks undermining authenticity and trust.
In professional and academic settings, transparency about AI assistance may be expected. Clear disclosure helps manage expectations and maintain ethical standards.
Maintaining Human Oversight
Ethical AI use depends on human judgment. Writers are responsible for verifying facts, assessing bias, and ensuring accuracy. AI tools cannot independently evaluate truth, fairness, or nuance, making human oversight indispensable.
Balancing efficiency with responsibility ensures that AI enhances writing quality rather than compromising it.
Emerging Trends in AI Writing Technology
AI writing tools continue to evolve, with new developments suggesting more personalized and integrated support for writers.
Personalized Writing Assistance
Future AI tools are likely to adapt more closely to individual writing styles. By learning preferred tone, sentence structure, and vocabulary, AI may offer suggestions that feel less generic and more aligned with the writer’s voice.
Predictive performance analysis may also become more common, allowing writers to estimate engagement or readability before publishing.
Enhanced Research Integration
AI tools are expected to improve research support by summarizing sources, organizing references, and identifying gaps in evidence. These capabilities can save time while strengthening content accuracy and depth.
AI in the Future of Journalism
In journalism, AI is likely to support investigative reporting by analyzing large datasets, identifying patterns, and drafting preliminary summaries. Personalization features may tailor news delivery to individual readers.
Despite these advances, editorial control and transparency will remain essential to preserving public trust.
Choosing the Right AI Writing Tool
Selecting an AI writing tool requires careful consideration. Not all tools offer the same features or align with every writing style.
Key Selection Criteria
Ease of use is critical. Tools should integrate smoothly into existing workflows without adding complexity. Tone control and customization options are also important, particularly for professional or academic writing.
Cost structures vary widely. Some tools offer subscriptions, while others charge per feature. Aligning tool capabilities with budget constraints prevents long-term frustration.
Practical Workflow for AI-Assisted Writing
A balanced workflow helps writers avoid generic output while maximizing AI benefits. Effective workflows typically involve three stages.
First, the writer defines goals, audience, and structure. Second, AI supports drafting, outlining, or editing. Third, the writer revises tone, logic, and flow to ensure originality and coherence.
This approach ensures that AI enhances efficiency without diminishing human creativity.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
Overreliance on AI can reduce quality and credibility. Common mistakes include publishing AI-generated drafts without review, trusting unverified facts, and ignoring audience needs.
Avoiding these pitfalls requires discipline, critical thinking, and a commitment to editorial standards.
The Future of AI in Content Writing
AI will continue to shape content writing, but its role is best defined as supportive rather than dominant. The most effective writers use AI to accelerate planning, drafting, and editing while maintaining control over ideas, tone, and final decisions.
By treating AI as a collaborative tool rather than a substitute, writers can navigate evolving demands without losing their voice. This balance ensures that content remains clear, ethical, and human, even as technology advances.
Conclusion:
Artificial intelligence has firmly established itself as a practical component of modern content writing, reshaping how ideas move from concept to publication. Its value lies not in replacing writers, but in reducing friction across the writing process by supporting research, drafting, editing, and consistency. When used with intention, AI enables writers to work more efficiently while preserving the depth, clarity, and purpose that audiences expect from high-quality content.
The long-term success of AI in content writing depends on balance. Writers who rely too heavily on automation risk producing generic or unreliable material, while those who ignore AI entirely may struggle to keep pace with evolving demands. Human judgment remains essential for shaping narrative direction, evaluating accuracy, and ensuring ethical responsibility. AI tools perform best when guided by clear goals, thoughtful prompts, and careful revision.
Looking ahead, the relationship between writers and AI will continue to mature. As tools become more adaptive and integrated into workflows, writers who understand both the capabilities and limitations of AI will gain a meaningful advantage. By treating AI as a collaborative assistant rather than an authority, content creators can protect originality, strengthen trust, and ensure that writing remains a human-driven craft in an increasingly automated world.
FAQs:
1. Does using AI in content writing reduce originality?
Using AI does not automatically reduce originality. Originality depends on how the tool is used. When writers treat AI as a drafting or editing assistant and apply their own ideas, insights, and revisions, the final content remains original and distinctive.
2. Can AI writing tools fully replace human writers?
AI writing tools cannot replace human writers because they lack true understanding, critical thinking, and contextual judgment. While AI can generate structured text and support efficiency, humans are essential for creativity, ethical decisions, and meaningful storytelling.
3. How can writers maintain their personal voice when using AI tools?
Writers maintain their voice by controlling prompts, revising AI output, and shaping tone and structure manually. AI works best when it supports the writing process rather than dictating the final language or message.
4. Are AI-generated texts reliable for factual accuracy?
AI-generated content should never be assumed to be fully accurate. Writers must verify facts, sources, and data independently. AI can assist with drafting, but responsibility for accuracy always remains with the writer.
5. Is it ethical to use AI tools for professional or academic writing?
Using AI tools is ethical when writers remain transparent, ensure originality, and retain accountability for the final work. Ethical concerns arise when AI output is submitted without review, disclosure, or proper attribution where required.
6. What types of writing benefit most from AI assistance?
AI is particularly useful for structured tasks such as outlines, summaries, SEO content, editing, and high-volume publishing. Complex analytical writing, opinion pieces, and investigative work still rely heavily on human expertise.
7. How will AI in content writing evolve in the coming years?
AI writing tools are expected to become more personalized, better at understanding tone preferences, and more integrated with research and performance analysis. Despite these advances, human oversight will remain central to quality and trust.
Gmail AI Inbox Feature Could Transform How You Manage Your Inbox
Google’s new AI Inbox for Gmail reimagines email management by using artificial intelligence to generate summaries, suggest tasks, and organize messages, offering a glimpse into the future of smarter, more efficient inboxes.
Introduction:
Email has remained one of the most resilient digital communication tools for decades, despite repeated predictions of its decline. While messaging apps, collaboration platforms, and social networks have changed how people communicate, email continues to serve as the backbone of professional, financial, and personal correspondence. Google’s introduction of an AI Inbox for Gmail suggests that the next major evolution of email will not be about replacing it, but about reinterpreting how information inside an inbox is organized, prioritized, and acted upon.
The new Google AI Inbox for Gmail replaces the familiar chronological list of emails with an AI-generated interface that surfaces summaries, action items, and topic groupings. Instead of asking users to scan subject lines and timestamps, the system attempts to interpret intent, urgency, and relevance. While the feature is still in early testing, it provides a revealing glimpse into how Google envisions the future of email productivity and AI-powered inbox management.
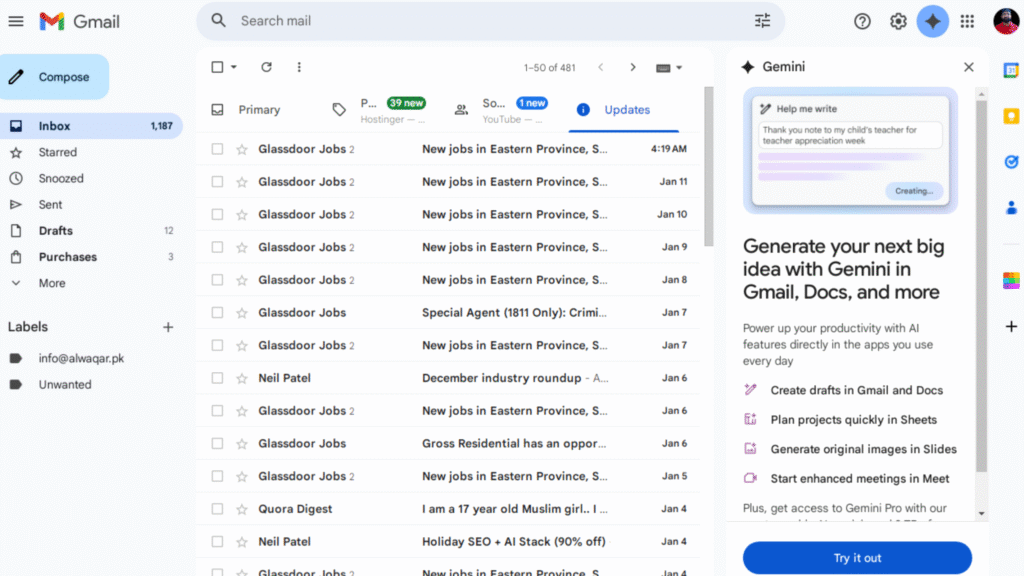
Understanding What Google’s AI Inbox Actually Is
At its core, the AI Inbox Gmail feature is not simply a cosmetic redesign. It represents a conceptual shift away from email as a static archive toward email as a dynamic task and information hub. Rather than displaying messages as individual units, the AI inbox view synthesizes content across multiple emails and presents it as digestible summaries and suggested actions.
When enabled, the traditional Gmail inbox is replaced by an AI-generated overview page. This page highlights suggested to-dos derived from message content, followed by broader topics that the system believes the user should review. Each suggestion links back to the original email, allowing users to dive deeper or respond directly if needed.
This approach positions Gmail less as a mailbox and more as an intelligent assistant that interprets communication on the user’s behalf. Google AI email tools are increasingly focused on reducing cognitive load, and the AI Inbox represents one of the most ambitious applications of that philosophy to date.
Limited Access and Early Testing Conditions
Currently, Google’s AI Inbox is available only to a small group of trusted testers. It is limited to consumer Gmail accounts and does not yet support Workspace users, who arguably represent the most demanding email audience. This restriction highlights the experimental nature of the feature and suggests that Google is proceeding cautiously before rolling it out at scale.
As with many experimental Gmail features, the current version may not reflect the final product. Early testers are effectively interacting with a prototype that is still learning how to interpret diverse inbox behaviors. This context is important when evaluating both the strengths and shortcomings of the AI Inbox Gmail experience.
Google has historically used limited testing phases to refine major Gmail updates, and the AI Inbox is likely to undergo significant iteration based on user feedback, performance metrics, and real-world usage patterns.
How AI-Generated Summaries Change Email Consumption
One of the most noticeable aspects of the AI Inbox is its reliance on AI-generated email summaries. Instead of reading each message individually, users are presented with condensed interpretations of content across multiple emails. These summaries aim to capture key points, deadlines, and requests without requiring users to open each message.
For users with high-volume inboxes, this approach could dramatically reduce time spent scanning emails. AI-based email organization allows the system to cluster related messages and surface the most relevant information first. In theory, this enables faster decision-making and more efficient inbox zero strategies.
However, summarization also introduces questions of accuracy and trust. Subtle nuances in tone, intent, or urgency can be lost when messages are condensed. While Google AI productivity tools have improved significantly, email remains a domain where small details can have outsized consequences.
Suggested To-Dos and Task-Oriented Email Design
Another defining feature of the AI Inbox for Gmail is its emphasis on actionable insights. Suggested to-dos appear prominently at the top of the inbox, encouraging users to treat email as a task list rather than a passive stream of messages.
These AI-generated tasks are based on inferred intent within emails, such as requests for responses, reminders to review documents, or time-sensitive notifications. By elevating these items, Gmail attempts to bridge the gap between communication and productivity tools.
This task-centric design aligns with broader trends in AI productivity software, where systems aim to reduce friction between information intake and action. Rather than requiring users to manually convert emails into tasks, the AI inbox view attempts to do that work automatically.
Still, this approach raises questions about user control. Not all users want their inbox to dictate their task priorities, and some may prefer the autonomy of deciding what deserves attention.
Topic Grouping and Contextual Awareness
Beyond individual to-dos, the AI Inbox organizes emails into topics that the system believes are worth reviewing. These topic clusters might include newsletters, ongoing conversations, financial updates, or recurring subscriptions.
This form of AI-driven email tools introduces contextual awareness into inbox management. Instead of treating each email as an isolated event, the system recognizes patterns and relationships over time. For users who receive frequent updates from the same sources, this could reduce redundancy and improve comprehension.
Topic grouping also reflects Google’s broader investment in contextual AI across its products. Similar principles are already visible in Google Search, Docs, and Calendar, where AI attempts to understand not just content, but intent and relevance.
Inbox Zero Meets Artificial Intelligence
For users who already maintain disciplined inbox zero systems, the AI Inbox Gmail experience presents an interesting paradox. On one hand, AI-powered inbox management promises to make inbox zero easier by highlighting what matters most. On the other hand, it introduces an additional interpretive layer that may not align with established personal workflows.
Users who prefer strict manual control may find the AI inbox view unnecessary or even intrusive. For these individuals, the traditional chronological list offers clarity and predictability that AI summaries cannot fully replicate.
This tension highlights an important truth about AI email management tools: effectiveness is highly subjective. What feels transformative for one user may feel redundant or disruptive for another.
Consumer Gmail Accounts Versus Professional Workflows
The current limitation of the AI Inbox to consumer Gmail accounts is notable. Personal inboxes tend to have lower volume and more predictable patterns than professional ones. Newsletters, personal reminders, and transactional emails are easier for AI systems to interpret than complex workplace communication.
Professional inboxes often involve ambiguous requests, layered conversations, and sensitive information that may challenge AI-based summarization. Until the AI Inbox is tested within Workspace environments, its suitability for enterprise use remains uncertain.
That said, Google’s decision to start with consumer Gmail suggests a strategy of gradual learning. By refining the system in simpler contexts, Google can improve accuracy before introducing it to higher-stakes professional settings.
Privacy, Trust, and AI Interpretation
Any discussion of AI-driven inbox view features must address privacy considerations. Gmail already processes email content for spam detection, categorization, and smart features, but deeper AI interpretation may heighten user concerns.
The AI Inbox relies on analyzing message content to generate summaries, tasks, and topics. While this processing occurs within Google’s existing infrastructure, users may still question how their data is being used and stored.
Trust is central to adoption. For the AI Inbox Gmail feature to succeed, users must believe that the system is not only accurate but also respectful of privacy boundaries. Transparent communication from Google about how AI email management tools operate will be critical.
Design Philosophy and the Future of Gmail
The AI Inbox is as much a design experiment as it is a technical one. By reimagining the inbox as an overview dashboard, Google is challenging long-standing assumptions about how email should look and function.
This redesign aligns with a broader trend toward proactive software. Instead of waiting for user input, systems increasingly anticipate needs and surface relevant information automatically. Gmail’s AI inbox view represents a clear step in that direction.
If successful, this approach could influence not only Gmail but email clients across the industry. Competitors may adopt similar AI-driven inbox organization strategies, accelerating a shift away from purely chronological email displays.
Why the AI Inbox May Not Be for Everyone
Despite its potential, the AI Inbox for Gmail is unlikely to appeal universally. Some users value the simplicity and transparency of a traditional inbox. Others may distrust automated prioritization or prefer to process emails manually.
Additionally, early versions of experimental Gmail features often struggle with edge cases. Misinterpreted emails, missed tasks, or irrelevant topic groupings could frustrate users and undermine confidence in the system.
The success of the AI Inbox will depend on how well Google balances automation with user agency. Providing customization options and clear explanations for AI decisions may help bridge this gap.
What This Means for the Evolution of Email
The introduction of Google AI Inbox for Gmail reflects a broader shift in how digital tools are evolving. As AI productivity tools become more capable, the role of software is moving from passive storage to active assistance.
Email, long criticized for inefficiency, may benefit significantly from this transformation. AI-generated summaries, task extraction, and contextual grouping address many of the pain points users associate with inbox overload.
However, the path forward will require careful design, ongoing refinement, and responsiveness to user feedback. Email is deeply personal, and any attempt to reshape it must respect diverse preferences and workflows.
Conclusion:
Google’s AI Inbox is not yet a finished product, nor is it a guaranteed replacement for the traditional Gmail experience. What it offers instead is a compelling preview of how AI-based email organization could redefine inbox management in the years ahead.
For some users, the AI inbox view may feel like a helpful assistant that brings clarity to a cluttered inbox. For others, it may remain an interesting experiment that never quite replaces familiar habits. Regardless of individual preference, the feature underscores Google’s commitment to integrating AI more deeply into everyday productivity tools.
As Google continues testing and refining its AI email management tools, the AI Inbox for Gmail stands as a meaningful signal: the future of email is not about fewer messages, but about smarter ways to understand and act on them.
FAQs:
1. What is Google AI Inbox for Gmail?
Google AI Inbox for Gmail is an experimental feature that uses artificial intelligence to organize emails, generate summaries, suggest tasks, and group related messages to make inbox management more efficient.
2. How does the AI Inbox Gmail feature work?
The AI Inbox analyzes your emails to identify key information, creates short summaries, highlights actionable tasks, and organizes emails into topics. Users can click each summary or task to access the original message.
3. Who can use Google AI Inbox?
Currently, the AI Inbox is available only to a limited number of trusted testers with consumer Gmail accounts. It is not yet available for Gmail Workspace or enterprise accounts.
4. Will AI Inbox replace the traditional Gmail interface?
Not entirely. The AI Inbox offers an alternative view of emails focused on summaries and tasks. Users can switch between the AI view and the standard chronological inbox based on their preference.
5. Can AI Inbox help achieve inbox zero faster?
Yes, by prioritizing emails and highlighting actionable items, AI Inbox can streamline email processing and help users maintain an organized inbox more efficiently than manual management alone.
6. How does AI Inbox handle privacy and security?
AI Inbox processes emails within Google’s existing Gmail infrastructure. Google emphasizes that content analysis for summaries and tasks is secure, but users should always review privacy guidelines for AI-driven features.
7. When will Google AI Inbox be available to everyone?
Google has not announced a specific public launch date. The feature is currently in early testing, and availability will likely expand gradually after user feedback and system improvements.
Google Pulls AI Overviews From Medical Searches After Accuracy Concerns
Google’s decision to disable AI Overviews for certain medical searches highlights growing concerns over the accuracy, safety, and responsibility of AI-generated health information in online search results.
Introduction:
Google’s decision to disable AI Overviews for certain medical queries marks a significant moment in the ongoing debate over artificial intelligence in healthcare-related search. Once promoted as a tool to simplify complex information, AI Overviews have increasingly come under scrutiny for producing misleading or incorrect medical guidance. Recent investigations and expert criticism have forced Google to reassess how AI-generated summaries operate when users search for health and medical information, an area where accuracy can directly affect patient outcomes.
The move follows mounting pressure from clinicians, researchers, and regulators who warn that AI-generated medical advice, when presented without sufficient context or verification, poses serious risks. While Google maintains that most AI Overviews provide reliable information, the removal of this feature from specific health searches suggests a growing acknowledgment that AI systems may not yet be equipped to handle the nuances of medical knowledge at scale.
The Rise of AI Overviews in Google Search
AI Overviews were introduced as part of Google’s broader push to integrate generative AI into its core search experience. The feature aims to provide concise, synthesized answers at the top of search results, drawing from multiple online sources to save users time and reduce the need to open multiple links.
In theory, AI Overviews were designed to enhance user experience, particularly for complex queries. However, in practice, the feature blurred the line between information aggregation and advisory content. For everyday topics, this approach proved convenient. In medical contexts, however, the same system raised concerns about oversimplification, missing context, and the amplification of inaccuracies.
Health-related searches represent one of the most sensitive categories in online information retrieval. Unlike general knowledge queries, medical searches often influence personal decisions about treatment, diet, testing, and medication. This places an exceptionally high burden of accuracy on any system generating health information.
Investigations That Sparked Alarm
Concerns around Google AI Overviews intensified after investigative reporting revealed several instances in which the feature provided incorrect or misleading medical advice. Experts reviewing these AI-generated summaries described some of the responses as alarming and potentially dangerous.
One widely cited example involved dietary guidance for pancreatic cancer patients. According to specialists, the AI Overview advised individuals with pancreatic cancer to avoid high-fat foods. Medical experts immediately flagged this recommendation as incorrect, noting that patients with pancreatic cancer often require higher fat intake due to impaired digestion. Following such advice could worsen nutritional deficiencies and increase health risks.
Another troubling case involved information about liver function tests. AI Overviews reportedly provided inaccurate explanations of normal test ranges, potentially leading individuals with serious liver conditions to believe their results were normal. Clinicians warned that such misinformation could delay diagnosis and treatment, with potentially severe consequences.
These examples underscored a broader issue: AI-generated summaries can appear authoritative while masking uncertainty, disagreement, or evolving medical consensus.
Google’s Response and Feature Removal
In the wake of public scrutiny, Google quietly disabled AI Overviews for certain medical queries. Searches such as those asking about normal liver blood test ranges no longer display AI-generated summaries, instead reverting to traditional search results.
Google declined to comment publicly on the specific removals, but company representatives reiterated their commitment to improving the quality of AI Overviews. According to Google, internal teams, including clinicians, regularly review feedback and evaluate the accuracy of AI-generated health information. The company has stated that while many AI Overviews are supported by reputable sources, gaps in context can occur, prompting ongoing adjustments and policy enforcement.
The selective removal of AI Overviews suggests a more cautious approach, particularly in areas where incorrect information could cause harm. Rather than fully abandoning the feature, Google appears to be refining where and how AI summaries are displayed.
Why Medical Searches Pose Unique Challenges for AI
Medical knowledge is complex, context-dependent, and constantly evolving. Symptoms, test results, and treatment recommendations often vary based on individual factors such as age, medical history, and coexisting conditions. AI systems trained on large datasets may struggle to account for these nuances, especially when generating generalized summaries.
Another challenge lies in the nature of online medical content itself. The internet contains a mix of peer-reviewed research, clinical guidelines, opinion pieces, outdated material, and outright misinformation. Even when AI models prioritize high-quality websites, they may still misinterpret or oversimplify findings.
Furthermore, medical language often involves probabilities and risk assessments rather than definitive answers. AI Overviews, designed to produce clear and concise summaries, may inadvertently remove critical caveats that clinicians rely on when interpreting health data.
The Risk of Authority Bias
One of the most concerning aspects of AI-generated medical information is the perception of authority. When an AI Overview appears at the top of search results, many users assume the information is verified and trustworthy, particularly when it comes from a platform as widely used as Google.
This authority bias can discourage users from consulting multiple sources or seeking professional medical advice. In healthcare, where misinterpretation can lead to delayed treatment or harmful self-management decisions, this dynamic presents a serious ethical challenge.
Experts argue that even small inaccuracies, when presented confidently, can have outsized consequences. Unlike traditional search results, which encourage comparison across sources, AI Overviews present a single synthesized narrative that may obscure disagreement or uncertainty.
A Pattern of AI Controversies
The medical misinformation issue is not an isolated incident in Google’s AI rollout. AI Overviews have previously drawn criticism for producing absurd or unsafe recommendations in non-medical contexts, including suggestions that defy basic logic or safety norms.
Beyond public ridicule, the feature has also faced legal challenges. Multiple lawsuits have accused AI-generated search content of causing harm, raising broader questions about liability and responsibility when automated systems provide advice-like information.
These controversies highlight the tension between innovation speed and risk management. As technology companies race to deploy generative AI features, the consequences of errors become increasingly visible, especially in high-stakes domains like health.
Implications for AI Safety in Healthcare
Google’s decision to pull AI Overviews from some medical searches may signal a broader shift in how technology companies approach AI safety in healthcare-related applications. Regulators and policymakers around the world are paying closer attention to how AI systems influence health decisions, even when they are not explicitly marketed as medical tools.
In many jurisdictions, health-related AI applications are subject to stricter oversight. While search engines traditionally fall outside medical device regulations, the introduction of AI-generated summaries complicates this distinction. When a system provides actionable health guidance, even indirectly, it begins to resemble a decision-support tool.
This evolving landscape raises important questions about standards, accountability, and transparency. Should AI-generated health information be labeled more clearly? Should certain topics be excluded entirely until higher accuracy thresholds are met? These debates are likely to intensify as AI becomes more deeply integrated into everyday digital experiences.
The Role of Clinicians and Human Oversight
One lesson emerging from this episode is the continued importance of human expertise in healthcare information delivery. While AI can assist with data aggregation and pattern recognition, it cannot replace clinical judgment or individualized assessment.
Google has emphasized that clinicians are involved in reviewing AI Overviews, but critics argue that post hoc review is insufficient. Instead, they advocate for stronger pre-deployment safeguards, clearer boundaries on use cases, and more conservative approaches to health-related AI features.
Some experts suggest that AI systems should focus on directing users to authoritative sources rather than summarizing medical guidance themselves. Others propose hybrid models in which AI-generated content is accompanied by prominent disclaimers and links to professional advice.
Public Trust and Platform Responsibility
Trust is a critical asset for any platform that provides health information. Once lost, it is difficult to rebuild. The controversy surrounding AI Overviews has prompted some users to question the reliability of AI-enhanced search results more broadly.
For Google, maintaining public trust means balancing innovation with caution. The company’s dominance in search amplifies the impact of any design decision, making even small errors highly visible and widely consequential.
By disabling AI Overviews for certain medical queries, Google appears to be acknowledging these stakes. Whether this move will be enough to restore confidence remains to be seen, especially as AI continues to evolve and expand into new areas.
What This Means for Users
For users searching for medical information, the removal of AI Overviews may result in a more traditional search experience, with links to individual websites rather than synthesized summaries. While this requires more effort, it may also encourage critical evaluation and cross-referencing.
Healthcare professionals continue to advise that online searches should not replace consultation with qualified medical providers. Search engines can offer general information, but diagnosis and treatment decisions should be guided by professionals who can assess individual circumstances.
The episode also serves as a reminder to approach AI-generated content with caution, particularly in areas where accuracy is paramount.
Looking Ahead: The Future of AI in Search
The challenges facing AI Overviews in medical searches reflect broader questions about the future of generative AI in search engines. As models become more powerful, expectations for reliability and responsibility will only increase.
Google is likely to continue refining its approach, experimenting with safeguards, topic restrictions, and improved evaluation methods. Other technology companies will be watching closely, as similar issues are likely to arise across platforms deploying AI-generated content.
Ultimately, the success of AI in search will depend not only on technical performance but also on ethical design choices and a willingness to prioritize user safety over rapid feature expansion.
Conclusion:
Google’s decision to pull AI Overviews from some medical searches represents a necessary course correction in the deployment of generative AI. While the technology holds promise for improving access to information, its limitations become starkly apparent in high-risk domains like healthcare.
The controversy underscores the need for caution, transparency, and human oversight when AI systems intersect with public health. As the digital landscape continues to evolve, this episode may serve as a defining example of why accuracy and responsibility must remain central to AI innovation.
FAQs:
1. Why did Google remove AI Overviews from some medical searches?
Google limited AI Overviews for certain health-related queries after reviews revealed that some summaries lacked proper medical context or contained inaccuracies that could mislead users and potentially cause harm.
2. What types of medical searches are affected by this change?
The removals primarily impact queries involving diagnostic information, test result interpretation, and disease-related guidance where incorrect summaries could influence medical decisions.
3. Are AI Overviews completely discontinued for health topics?
No, Google has not eliminated AI Overviews across all health searches. The company appears to be selectively restricting the feature in higher-risk medical areas while continuing to refine its accuracy standards.
4. How can incorrect AI-generated medical information be harmful?
When presented as authoritative, inaccurate health summaries may delay proper diagnosis, encourage unsafe self-treatment, or create false reassurance, especially for users managing serious conditions.
5. What steps is Google taking to improve AI health information accuracy?
Google says it relies on internal review teams, including clinicians, and applies policy-based adjustments when AI summaries miss context or fail to meet quality expectations.
6. Does this change affect how users should search for medical information online?
The update reinforces the importance of consulting multiple trusted sources and seeking professional medical advice rather than relying solely on automated summaries.
7. What does this mean for the future of AI in healthcare-related search?
The move signals a more cautious approach to deploying generative AI in health contexts, suggesting future systems may include stronger safeguards, clearer limitations, and increased human oversight.