This article examines the historical development of artificial intelligence, outlining the technological shifts, innovation cycles, and real-world adoption that shaped AI through 2025.
History of Artificial Intelligence: A Century-Long Journey to Intelligent Systems (Up to 2025)
Artificial intelligence has transitioned from philosophical speculation to a foundational technology shaping global economies and digital societies. Although AI appears to be a modern phenomenon due to recent breakthroughs in generative models and automation, its origins stretch back more than a century. The evolution of artificial intelligence has been shaped by cycles of optimism, limitation, reinvention, and accelerated progress, each contributing to the systems in use today.
This report presents a comprehensive overview of the history of artificial intelligence, tracing its development from early conceptual ideas to advanced AI agents operating in 2025. Understanding this journey is essential for grasping where AI stands today and how it is likely to evolve in the years ahead.
Understanding Artificial Intelligence
Artificial intelligence refers to the capability of machines and software systems to perform tasks that traditionally require human intelligence. These tasks include reasoning, learning from experience, recognizing patterns, understanding language, making decisions, and interacting with complex environments.
Unlike conventional computer programs that rely on fixed instructions, AI systems can adapt their behavior based on data and feedback. This adaptive capability allows artificial intelligence to improve performance over time and operate with varying degrees of autonomy. Modern AI includes a broad range of technologies such as machine learning, deep learning, neural networks, natural language processing, computer vision, and autonomous systems.
Early Philosophical and Mechanical Foundations
The concept of artificial intelligence predates digital computing by centuries. Ancient philosophers explored questions about cognition, consciousness, and the nature of thought, laying conceptual groundwork for later scientific inquiry. In parallel, inventors across civilizations attempted to create mechanical devices capable of independent motion.
Early automatons demonstrated that machines could mimic aspects of human or animal behavior without continuous human control. These mechanical creations were not intelligent in the modern sense, but they reflected a persistent human desire to reproduce intelligence artificially. During the Renaissance, mechanical designs further blurred the boundary between living beings and engineered systems, reinforcing the belief that intelligence might be constructed rather than innate.
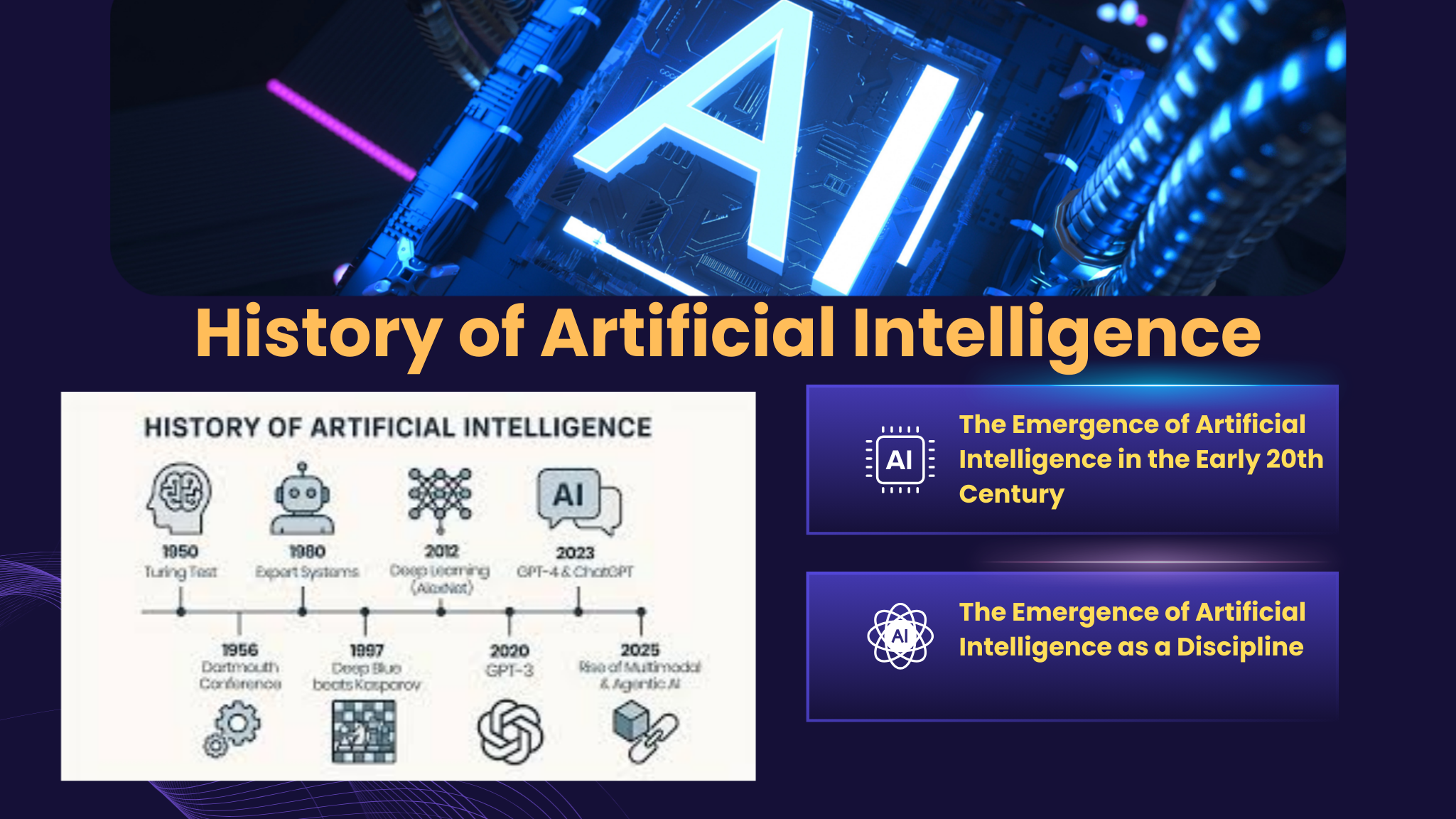
The Emergence of Artificial Intelligence in the Early 20th Century
The early 1900s marked a shift from philosophical curiosity to technical ambition. Advances in engineering, mathematics, and logic encouraged scientists to explore whether human reasoning could be formally described and replicated. Cultural narratives began portraying artificial humans and autonomous machines as both marvels and warnings, shaping public imagination.
During this period, early robots and electromechanical devices demonstrated limited autonomy. Although their capabilities were minimal, they inspired researchers to consider the possibility of artificial cognition. At the same time, foundational work in logic and computation began to define intelligence as a process that could potentially be mechanized.
The Emergence of Artificial Intelligence as a Discipline
Funding plummeted as both corporations and governments pulled back support, citing unfulfilled projections and technological constraints.
The development of programmable computers during and after World War II provided the technical infrastructure needed to experiment with machine reasoning. A pivotal moment came when researchers proposed that machine intelligence could be evaluated through observable behavior rather than internal processes. This idea challenged traditional views of intelligence and opened the door to experimental AI systems. Shortly thereafter, artificial intelligence was formally named and recognized as a distinct research discipline.
Early AI programs focused on symbolic reasoning, logic-based problem solving, and simple learning mechanisms. These systems demonstrated that machines could perform tasks previously thought to require human intelligence, fueling optimism about rapid future progress.
Symbolic AI and Early Expansion
From the late 1950s through the 1960s, artificial intelligence research expanded rapidly. Scientists developed programming languages tailored for AI experimentation, enabling more complex symbolic manipulation and abstract reasoning.
During this period, AI systems were designed to solve mathematical problems, prove logical theorems, and engage in structured dialogue. Expert systems emerged as a prominent approach, using predefined rules to replicate the decision-making processes of human specialists.
AI also entered public consciousness through books, films, and media, becoming synonymous with futuristic technology. However, despite promising demonstrations, early systems struggled to handle uncertainty, ambiguity, and real-world complexity.
Funding Challenges and the First AI Slowdown
By the early 1970s, limitations in artificial intelligence became increasingly apparent. Many systems performed well in controlled environments but failed to generalize beyond narrow tasks. Expectations set by early researchers proved overly ambitious, leading to skepticism among funding agencies and governments.
As investment declined, AI research experienced its first major slowdown. This period highlighted the gap between theoretical potential and practical capability. Despite reduced funding, researchers continued refining algorithms and exploring alternative approaches, laying the groundwork for future breakthroughs.
Commercial Interest and the AI Boom
The 1980s brought renewed enthusiasm for artificial intelligence. Improved computing power and targeted funding led to the commercialization of expert systems. These AI-driven tools assisted organizations with decision-making, diagnostics, and resource management.
Businesses adopted AI to automate specialized tasks, particularly in manufacturing, finance, and logistics. At the same time, researchers advanced early machine learning techniques and explored neural network architectures inspired by the human brain.
This era reinforced the idea that AI could deliver tangible economic value. However, development costs remained high, and many systems were difficult to maintain, setting the stage for another period of disappointment.
The AI Winter and Lessons Learned
The late 1980s and early 1990s marked a period known as the AI winter. The formal establishment of artificial intelligence took place in the mid-1900s, defining it as a distinct area of research. Specialized AI hardware became obsolete as general-purpose computers grew more powerful and affordable. Many AI startups failed, and public interest waned. Despite these challenges, the AI winter proved valuable in refining research priorities and emphasizing the importance of scalable, data-driven approaches.
Crucially, this period did not halt progress entirely. Fundamental research continued, enabling the next wave of AI innovation.
The Rise of Intelligent Agents and Practical AI
The mid-1990s signaled a resurgence in artificial intelligence. Improved algorithms, faster processors, and increased data availability allowed AI systems to tackle more complex problems.
One landmark achievement demonstrated that machines could outperform humans in strategic domains. AI agents capable of planning, learning, and adapting emerged in research and commercial applications. Consumer-facing AI products also began entering everyday life, including speech recognition software and domestic robotics.
The internet played a transformative role by generating massive amounts of data, which became the fuel for modern machine learning models.
Machine Learning and the Data-Driven Shift
As digital data volumes exploded, machine learning emerged as the dominant paradigm in artificial intelligence. Instead of relying on manually coded rules, systems learned patterns directly from data.
Supervised learning enabled accurate predictions, unsupervised learning uncovered hidden structures, and reinforcement learning allowed agents to learn through trial and error. These techniques expanded AI’s applicability across industries, from healthcare and finance to marketing and transportation.
Organizations increasingly viewed AI as a strategic asset, integrating analytics and automation into core operations.
Deep Learning and the Modern AI Revolution
The 2010s marked a turning point with the rise of deep learning. Advances in hardware, particularly graphics processing units, enabled the training of large neural networks on massive datasets.
Deep learning systems achieved unprecedented accuracy in image recognition, speech processing, and natural language understanding. AI models began generating human-like text, recognizing objects in real time, and translating languages with remarkable precision.
These breakthroughs transformed artificial intelligence from a specialized research area into a mainstream technology with global impact.
Generative AI and Multimodal Intelligence
The early 2020s introduced generative AI systems capable of producing text, images, audio, and code. These models blurred the line between human and machine creativity, accelerating adoption across creative industries, education, and software development.
Multimodal AI systems integrated multiple forms of data, enabling richer understanding and interaction. Conversational AI tools reached mass audiences, reshaping how people search for information, create content, and interact with technology.
At the same time, concerns about ethics, bias, transparency, and misinformation gained prominence, prompting calls for responsible AI governance.
Artificial Intelligence in 2025: The Era of Autonomous Agents
By 2025, artificial intelligence has entered a new phase characterized by autonomous AI agents. These systems are capable of planning, executing, and adapting complex workflows with minimal human intervention.
AI copilots assist professionals across industries, from software development and finance to healthcare and operations. Businesses increasingly rely on AI-driven insights for decision-making, forecasting, and optimization.
While current systems remain narrow in scope, their growing autonomy raises important questions about accountability, trust, and human oversight.
Societal Impact and Ethical Considerations
As artificial intelligence becomes more integrated into daily life, its societal implications have intensified. Automation is reshaping labor markets, creating both opportunities and challenges. Ethical concerns surrounding data privacy, algorithmic bias, and AI safety have become central to public discourse.
Governments and institutions are working to establish regulatory frameworks that balance innovation with responsibility. Education and reskilling initiatives aim to prepare the workforce for an AI-driven future.
Looking Ahead: The Future of Artificial Intelligence
The future of artificial intelligence remains uncertain, but its trajectory suggests continued growth and integration. Advances in computing, algorithms, and data infrastructure will likely drive further innovation.
Rather than replacing humans entirely, AI is expected to augment human capabilities, enhancing productivity, creativity, and decision-making. The pursuit of artificial general intelligence continues, though significant technical and ethical challenges remain.
Understanding the history of artificial intelligence provides critical context for navigating its future. The lessons learned from past successes and failures will shape how AI evolves beyond 2025.
Date-Wise History of Artificial Intelligence (1921–2025)
Early Conceptual Era (1921–1949)
This phase introduced the idea that machines could imitate human behavior, primarily through literature and mechanical experimentation.
Year | Key Development |
1921 | The idea of artificial workers entered public imagination through fiction |
1929 | Early humanoid-style machines demonstrated mechanical autonomy |
1949 | Scientists formally compared computing systems to the human brain |
Birth of Artificial Intelligence (1950–1956)
This era established AI as a scientific discipline.
Year | Key Development |
1950 | A behavioral test for machine intelligence was proposed |
1955 | Artificial intelligence was officially defined as a research field |
Symbolic AI and Early Growth (1957–1972)
Researchers focused on rule-based systems and symbolic reasoning.
Year | Key Development |
1958 | The first programming language designed for AI research emerged |
1966 | Early conversational programs demonstrated language interaction |
First Setback and Reduced Funding (1973–1979)
Unmet expectations resulted in declining support.
Year | Key Development |
1973 | Governments reduced AI funding due to limited real-world success |
1979 | Autonomous navigation systems were successfully tested |
Commercial Expansion and AI Boom (1980–1986)
AI entered enterprise environments.
Year | Key Development |
1980 | Expert systems were adopted by large organizations |
1985 | AI-generated creative outputs gained attention |
AI Winter Period (1987–1993)
Investment and interest declined significantly.
Year | Key Development |
1987 | Collapse of specialized AI hardware markets |
1988 | Conversational AI research continued despite funding cuts |
Practical AI and Intelligent Agents (1994–2010)
AI systems began outperforming humans in specific tasks.
Year | Key Development |
1997 | AI defeated a human world champion in chess |
2002 | Consumer-friendly home robotics reached the market |
2006 | AI-driven recommendation engines became mainstream |
2010 | Motion-sensing AI entered consumer entertainment |
Data-Driven AI and Deep Learning Era (2011–2019)
AI performance improved dramatically with data and computing power.
Year | Key Development |
2011 | AI systems demonstrated advanced language comprehension |
2016 | Socially interactive humanoid robots gained global visibility |
2019 | AI achieved elite-level performance in complex strategy games |
Generative and Multimodal AI (2020–2022)
AI systems began creating content indistinguishable from human output.
Year | Key Development |
2020 | Large-scale language models became publicly accessible |
2021 | AI systems generated images from text descriptions |
2022 | Conversational AI reached mass adoption worldwide |
AI Integration and Industry Transformation (2023–2024)
AI shifted from tools to collaborators.
Year | Key Development |
2023 | Multimodal AI combined text, image, audio, and video understanding |
2024 | AI copilots embedded across business, software, and productivity tools |
Autonomous AI Agents Era (2025)
AI systems began executing complex workflows independently.
Year | Key Development |
2025 | AI agents capable of planning, reasoning, and autonomous execution emerged |
Conclusion:
Artificial intelligence has evolved through decades of experimentation, setbacks, and breakthroughs, demonstrating that technological progress is rarely linear. From early philosophical ideas and mechanical inventions to data-driven algorithms and autonomous AI agents, each phase of development has contributed essential building blocks to today’s intelligent systems. Understanding this historical progression reveals that modern AI is not a sudden innovation, but the result of sustained research, refinement, and adaptation across generations.
As artificial intelligence reached broader adoption, its role expanded beyond laboratories into businesses, public services, and everyday life. Advances in machine learning, deep learning, and generative models transformed AI from a specialized tool into a strategic capability that supports decision-making, creativity, and operational efficiency. At the same time, recurring challenges around scalability, ethics, and trust underscored the importance of responsible development and realistic expectations.
Looking ahead, the future of artificial intelligence will be shaped as much by human choices as by technical capability. While fully general intelligence remains an aspirational goal, the continued integration of AI into society signals a lasting shift in how technology supports human potential. By learning from its past and applying those lessons thoughtfully, artificial intelligence can continue to evolve as a force for innovation, collaboration, and long-term value.
FAQs:
1. What is meant by the history of artificial intelligence?
The history of artificial intelligence refers to the long-term development of ideas, technologies, and systems designed to simulate human intelligence, spanning early mechanical concepts, rule-based computing, data-driven learning, and modern autonomous AI systems.
2. When did artificial intelligence officially begin as a field?
Artificial intelligence became a recognized scientific discipline in the mid-20th century when researchers formally defined the concept and began developing computer programs capable of reasoning, learning, and problem solving.
3. Why did artificial intelligence experience periods of slow progress?
AI development faced slowdowns when expectations exceeded technical capabilities, leading to reduced funding and interest. These periods highlighted limitations in computing power, data availability, and algorithm design rather than a lack of scientific potential.
4. How did machine learning change the direction of AI development?
Machine learning shifted AI away from manually programmed rules toward systems that learn directly from data. This transition allowed AI to scale more effectively and perform well in complex, real-world environments.
5. What role did deep learning play in modern AI breakthroughs?
Deep learning enabled AI systems to process massive datasets using layered neural networks, leading to major improvements in speech recognition, image analysis, language understanding, and generative applications.
6. How is artificial intelligence being used in 2025?
In 2025, artificial intelligence supports autonomous agents, decision-making tools, digital assistants, and industry-specific applications, helping organizations improve efficiency, accuracy, and strategic planning.
7. Is artificial general intelligence already a reality?
Artificial general intelligence remains a theoretical goal. While modern AI systems perform exceptionally well in specific tasks, they do not yet possess the broad reasoning, adaptability, and understanding associated with human-level intelligence.