-
-
-
Microsoft Copilot Tasks AI Manages Tasks Easily
Microsoft Copilot Tasks AI is a new cloud-based assistant designed … Read more
-
X AI Generated Content Crackdown Begins
X AI Generated Content is becoming a major focus as … Read more
-
Trump Pushes AI Data Centers Power Supply Plan
This report explains how President Donald Trump is urging major … Read more
-
Adobe AI Video Editing Tool Launches Quick Cut
This article explains how Adobe’s new AI video editing tool … Read more
-
Anthropic Accuses China’s DeepSeek of AI Model Distillation
This report examines the growing controversy over AI model distillation, … Read more
-
Google AI Music Maker Now in Gemini App
Google AI music maker An in-depth look at how Google’s … Read more
-
-
Gmail AI Inbox Feature Could Transform How You Manage Your Inbox
Google’s new AI Inbox for Gmail reimagines email management by … Read more
-
Google Pulls AI Overviews From Medical Searches After Accuracy Concerns
Google’s decision to disable AI Overviews for certain medical searches … Read more
-
Gemini on Google TV Update Brings Nano Banana AI and Smart Voice Features
Google’s latest Gemini on Google TV update introduces generative AI … Read more
-
LG CLOiD Home Robot at CES: AI-Powered Laundry, Cooking, and Home Automation
At CES, LG unveils its CLOiD home robot, offering a … Read more
-
How Leonardo.Ai Empowers Creators with Smart AI Design and Marketing Solutions
Discover how Leonardo.Ai is revolutionizing the world of marketing and … Read more
-
-
A New Era for Google Photos AI and Android XR
Google Photos is stepping into a new era powered by … Read more
-
AI Agents Social Network Emerges, Redefining Digital Interaction
This article explores the emergence of an AI agents social … Read more
-
-
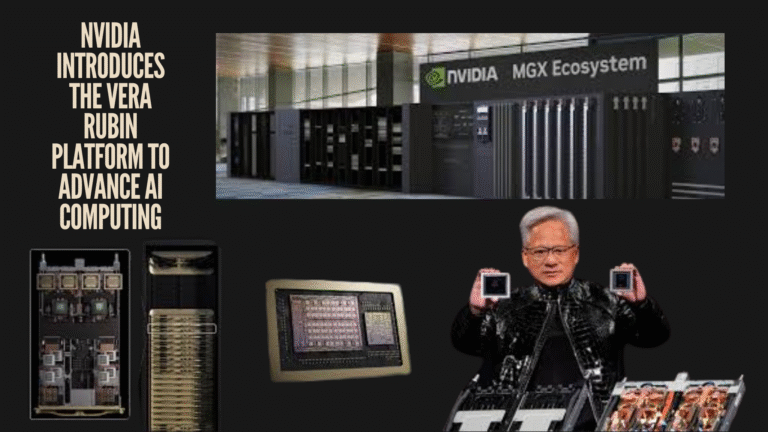
Nvidia Introduces the Vera Rubin Platform to Advance AI Computing
This report explores Nvidia’s early unveiling of the Vera Rubin … Read more
-
Lenovo Qira AI Assistant Can Act on Your Behalf Across Devices
Lenovo’s latest CES announcement introduces Qira, a system-level, cross-device AI … Read more
-
Lenovo AI Glasses Concept Unveiled at CES 2026
Lenovo has unveiled a concept pair of AI-powered smart glasses … Read more
-
AI Foreign Policy and National Security: Jake Sullivan on US-China Tech Risks
“Former White House adviser Jake Sullivan warns that reversing US … Read more
-
Character.AI and Google Reach Settlement in Teen Suicide Lawsuits
This report examines how Character.AI and Google are resolving multiple … Read more
-
Google Gemini Buy Buttons Signal a New Era of AI Shopping
Google is expanding Gemini into a transactional platform, bringing AI-powered … Read more
-
Claude Cowork Brings Practical AI Agents to Everyday Workflows
Anthropic’s latest Claude Cowork feature signals a shift toward practical … Read more
-
UK Deepfake Law Targets AI-Created Nudes Amid Grok Controversy
The UK is enforcing a new law that makes the … Read more
-
X Faces Scrutiny as Grok Deepfake Images Continue to Surface
Despite X’s assurances of tighter AI controls, this article examines … Read more
-
Advocacy Groups Urge Apple, Google to Act on Grok Deepfake Abuse
A growing coalition of advocacy groups is urging Apple and … Read more
-
Australia Teen Social Media Ban Forces Meta Crackdown
Australia’s new teen social media ban is reshaping how global … Read more
-
-
-
Google AI Videomaker Flow Expands to Workspace Users
Google has expanded its AI video creation tool Flow to … Read more
-
Grok AI Controversy Exposes AI Safety Gaps
A closer look at how Grok’s rapid rollout and limited … Read more
-
OpenAI Practical Adoption Becomes Core Focus for 2026
OpenAI is reshaping its long-term strategy around a single objective: … Read more
-
Sen. Markey Challenges OpenAI Over ChatGPT Advertising Practices
U.S. Senator Sen. Ed Markey has formally raised concerns over … Read more
-
Meta Temporarily Blocks Teen Access to AI Characters
Meta has announced a temporary pause on teen access to … Read more
-
Gemini Personal Intelligence Brings Smarter AI Assistants
This report examines Google Gemini’s new Personal Intelligence feature, its … Read more
-
-
Elon Musk’s xAI Lays Off 500 Workers in Major Restructuring
In a sweeping move that signals a new direction for … Read more