- When was imo launched?
- Who developed imo?
- What is the primary function of imo?
- How many messages are sent through imo per day?
- What makes imo popular among users?
- What does “IMO” stand for?
- What is the International Maritime Organization (IMO)?
- What types of files can be sent through imo?
- How many participants can join encrypted group voice and video calls on imo?
- Is imo blocked in the UAE?
- Why are VoIP apps blocked in the UAE?
- Is FaceTime allowed in Dubai?
- Where are VPNs illegal?
- Why is it recommended to use a VPN with imo?
- Does imo require a SIM card?
- What are some drawbacks of using imo?
- Which operating systems is imo accessible from?
- Is imo considered a secure app?
- How many teams participated in the event on July 12th?
- How much funding did imo raise in 2013?
- When was the Windows version of imo released?
- How many installs did imo reach by January 2018?
- What was the original purpose of imo when it was launched in 2005?
- Which messaging networks did imo initially support?
- Who is responsible for the development of imo?
- How does imo verify user accounts?
- How can users access their call history on imo?
- What caution should be exercised when using video calling apps?
- How does imo handle user data privacy?
- What is the significance of imo reaching 500 million installs in January 2018?
- In which country was imo initially launched?
- How many users does imo currently have?
- What is the advantage of using imo over other communication platforms?
- What features does imo offer besides instant messaging and video calling?
- What role does PageBites play in the development of imo?
- Why are VPNs banned in certain countries?
- How does imo ensure security during group calls?
- How does imo support users with low network signals?
- What are some potential risks of using imo?
- How does imo compare to other video calling apps in terms of quality?
- What platforms is imo compatible with?
- How does imo handle user feedback and suggestions?
- What measures does imo take to prevent cyber fraud?
- Can users access imo on desktop computers?
- How does imo ensure data encryption during calls?
- What distinguishes imo’s sticker collection?
- How does imo contribute to global communication?
- What steps can users take to protect their privacy while using imo?
- How does imo handle user complaints regarding call quality?
- What strategies does imo employ to attract new users?
- How does imo address issues related to battery drain?
- What is imo’s policy on sharing user data with third parties?
- How does imo handle account verification?
- How does imo address concerns about data security?
- Can users access their chat history on imo?
- How does imo handle reports of inappropriate behavior?
- How does imo ensure service reliability during peak usage times?
- What measures does imo take to prevent unauthorized access to user accounts?
- How does imo address concerns about potential hacking?
- What support options are available for imo users experiencing technical issues?
- How does imo monitor and address instances of spam or phishing attempts?
- What steps does imo take to comply with data protection regulations?
- How does imo handle reports of harassment or bullying within the platform?
- What resources does imo provide for users to learn about privacy and security best practices?
- How does imo collaborate with law enforcement agencies to address illegal activities conducted through the platform?
Introduction to imo:
Inaugurated in 2007 within the United States, imo, developed by PageBites, has emerged as a prominent force in the realm of instant messaging and video calling. With a staggering user base exceeding 200 million individuals, the platform witnesses the exchange of over 50 million messages each day. Its reputation for simplicity and effective communication tools has positioned imo as a favored choice for individuals seeking a dependable and user-friendly means of connectivity. The platform’s resounding success in accumulating such a vast user base serves as a testament to its allure and practicality in the digital communication arena, offering users a seamless avenue to partake in real-time conversations and video calls on a global scale.

Recognized Simplicity and Efficiency: Renowned for its simplicity and efficient communication features, imo has garnered widespread acclaim among users seeking a reliable and user-friendly platform for staying connected. Its intuitive interface and seamless functionality make it a preferred choice for users across the globe.
Understanding the Name “imo”: The acronym “IMO,” which stands for “in my opinion,” reflects the platform’s commitment to fostering candid and straightforward communication among its users. This simple yet meaningful designation resonates with the platform’s ethos of enabling honest and open dialogue.
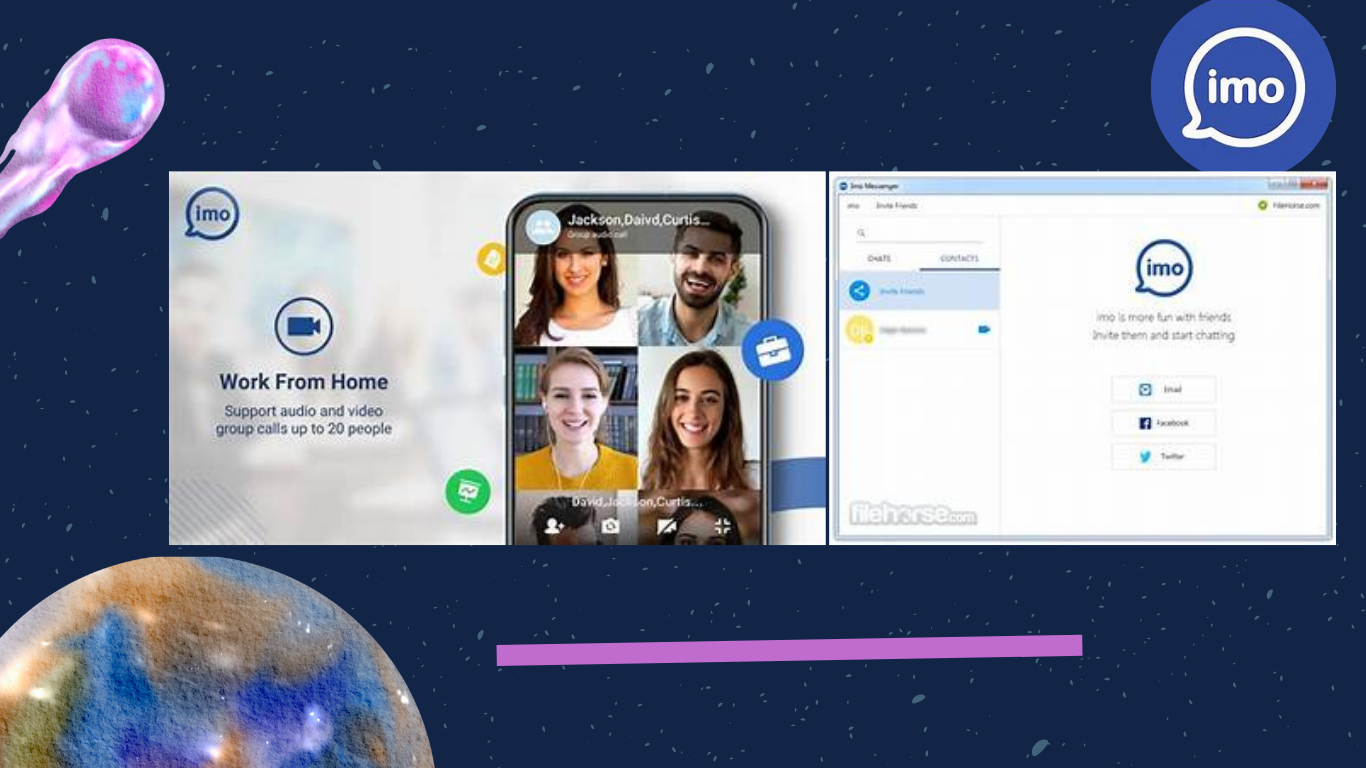
Features and Functionality: As a proprietary video/audio call and instant messaging software service, imo offers a diverse range of features to enhance communication. Users can send text or voice messages, make video calls, and share files such as videos, music, PDFs, and stickers, thereby facilitating versatile and engaging interactions.
Group Communication: imo supports encrypted group voice and video calls with up to 20 participants, catering to the needs of larger groups for collaborative discussions and virtual gatherings.
Advantages of imo: The advantages of imo lie in its simplicity, security, and speed. Serving as a free, secure, and faster international video call and instant messaging app, imo enables users to connect easily and quickly with friends, family, and other contacts worldwide, even under challenging network conditions.
Developer Information: imo is developed and operated by PageBites, Inc., a California-based company dedicated to providing users with a seamless and secure communication experience. Operating under the name “imo,” the company remains committed to innovation and user satisfaction.
Regional Restrictions and Considerations: While imo offers significant benefits to users globally, it may be subject to regional restrictions in certain areas. For instance, in the United Arab Emirates (UAE), imo, along with other VoIP apps, is blocked to protect the interests of local telecommunication companies.
Legal Implications and VPN Usage: In regions where imo is not explicitly banned, users may still need to consider legal implications, especially concerning the use of virtual private networks (VPNs). While VPN usage is illegal in some countries, it may be necessary for accessing imo in restricted areas while ensuring privacy and security.
Security and Privacy Measures: imo prioritizes user security and privacy, implementing end-to-end encryption for chats and calls to safeguard sensitive communications. Additionally, user accounts are verified through phone numbers, adding an extra layer of authentication and protection against unauthorized access.
Drawbacks and Limitations: Despite its advantages, imo has faced criticism for privacy issues, battery drain, poor quality, and limited features compared to other video calling apps. Users should weigh these factors carefully when selecting imo as their preferred communication platform.
Global Accessibility and Installation Milestones: imo is fully accessible across various operating systems, including Android, iOS, Windows, and MacOS, ensuring seamless connectivity for users worldwide. The platform reached a significant milestone in January 2018 with 500 million installations, reflecting its widespread popularity and adoption.
Usage Recommendations for Safety: To ensure safe and secure usage of imo and similar platforms, users are advised to exercise caution when interacting with unknown individuals, avoid sharing personal information online, and utilize secure platforms for video calling to mitigate the risk of cyber fraud and privacy breaches.
History:
- Inception of imo.im: In the digital era of 2005, imo.im emerged as a groundbreaking web-based application, heralding a new era in online messaging. Its debut marked a significant departure from traditional communication methods, laying the foundation for a more interconnected world.
- Unified Chat Platform: Imo.im revolutionized the way people communicate by providing a unified chat platform, seamlessly integrating various messaging services into one centralized interface. This innovation simplified the user experience, eliminating the need to navigate between multiple applications.
- Seamless Multichat Access: Users embraced imo.im for its unparalleled ability to facilitate messaging across different platforms without the hassle of individual sign-ups. This seamless multichat access empowered users to connect with friends and colleagues regardless of their preferred messaging service.
- Streamlined User Experience: One of imo.im’s key strengths was its focus on delivering a streamlined user experience. By consolidating multiple chat platforms into a single interface, imo.im enhanced accessibility and convenience, making communication effortless and efficient.
- Preservation of Chat History: A standout feature of imo.im was its provision for users to archive chat history, ensuring that conversations were preserved for future reference. This feature proved invaluable for users who relied on imo.im for both personal and professional communication.
- Supported Platforms: From its inception, imo.im boasted compatibility with a wide array of platforms, including Facebook Messenger, Google Talk, Yahoo! Messenger, and Skype. This broad support ensured that users could connect with friends and contacts regardless of their preferred messaging service.
- Skype Integration: Imo.im’s integration of Skype further solidified its position as a comprehensive communication solution. By incorporating Skype into its platform, imo.im enabled users to seamlessly interact with contacts across different networks, fostering greater connectivity.
- Impact of Microsoft Acquisition: The landscape shifted with Microsoft’s acquisition of Skype, leading to the discontinuation of Skype support on imo.im. This pivotal development marked a significant turning point for the platform, prompting a reassessment of its strategic direction.
- Third-Party Support Cessation: In a strategic move in March 2014, imo.im decided to discontinue support for all third-party messaging networks. This decision reshaped imo.im’s focus, allowing it to concentrate on enhancing its core features and user experience.
- Financial Milestone: Imo.im reached a significant milestone in 2013 when it secured a substantial funding round of $13.3 million. This infusion of capital underscored investor confidence in imo.im’s vision and potential for growth.
- Expansion to Windows: The evolution of imo.im continued with the introduction of its Windows version in July 2016. This expansion broadened imo.im’s reach, catering to a wider audience of users across different operating systems.
- Developer Background: Imo.im was developed by Pagebites, a subsidiary of Singularity IM, Inc. The expertise and innovation of the development team behind imo.im played a pivotal role in shaping its success and evolution.
- Account Verification: To ensure the security and authenticity of its users, imo.im implemented a mandatory account verification process using phone numbers. This measure enhanced user trust and safety within the platform.
- Exponential Growth: By January 2018, imo.im had surpassed a monumental milestone with 500 million installations worldwide. This exponential growth highlighted imo.im’s widespread adoption and popularity among users globally.
Enhanced Privacy Measures:
imo.im has taken significant strides to prioritize user privacy by implementing end-to-end encryption for both chats and calls. This robust security measure guarantees that conversations remain confidential and inaccessible to any third-party entities. With end-to-end encryption in place, imo.im ensures that only the intended sender and receiver have access to the content of their communications, enhancing user trust and confidence in the platform’s commitment to safeguarding privacy.
Aspect | Details |
Launch | In 2005, imo.im debuted as a web-based application, revolutionizing online messaging. |
Unified Interface | Users accessed various chat platforms through a single interface, streamlining communication. |
Multichat Access | Messaging across multiple platforms was enabled without individual sign-ups. |
Chat History Storage | Users conveniently preserved chat history for future reference within the application. |
Supported Platforms | Supported platforms included Facebook Messenger, Google Talk, Yahoo! Messenger, and Skype. |
Skype Integration | Skype was initially supported until its withdrawal post-Microsoft acquisition. |
Third-Party Support Cessation | In March 2014, imo.im ceased support for all third-party messaging networks. |
Funding | The platform secured $13.3 million in funding in 2013, signifying investor confidence. |
Windows Version | Pagebites introduced the Windows version in July 2016, expanding accessibility. |
Developer Background | Developed by Pagebites, a subsidiary of Singularity IM, Inc., ensuring expertise in development. |
Account Verification | User accounts required phone number verification for enhanced security. |
Installations | By January 2018, imo.im had amassed 500 million installations globally. |
Conclusion:
In conclusion, imo has established itself as a prominent player in the realm of instant messaging and video calling since its inception in 2007. Developed by PageBites, Inc., imo has garnered a user base of 200 million individuals, with over 50 million messages sent daily, highlighting its widespread adoption and utility in facilitating seamless communication across the globe. Its simplicity, efficient features, and user-friendly interface have contributed to its popularity among users seeking reliable means of staying connected in real-time.
Despite its advantages, imo faces challenges such as being blocked in certain regions like the UAE, where VoIP apps are restricted to protect the interests of local telecom companies. However, users in such regions can still leverage VPNs to access imo’s services, albeit with caution due to legal implications in some countries.
Moreover, imo’s compatibility with various devices and networks enables users to connect with friends and family worldwide, transcending geographical boundaries. Its support for encrypted group voice and video calls adds a layer of security and privacy to users’ conversations, enhancing the overall experience.
While imo offers free and unlimited messaging and calling features, it is not without its drawbacks, including privacy concerns, battery drain issues, and limited functionalities compared to other video calling apps. Despite these limitations, imo remains a viable option for users seeking a secure platform for communication.
Looking ahead, imo continues to evolve, with updates and enhancements aimed at addressing user feedback and improving the overall user experience. Its journey from a web-based application to a widely used messaging platform underscores its adaptability and commitment to meeting the evolving needs of its user base.
In summary, imo’s journey from its inception to its current standing as a leading communication platform reflects its resilience, innovation, and dedication to providing users with a seamless and secure means of staying connected in today’s digital landscape.

Prof. Mian Waqar Ahmad
Prof. Mian Waqar Ahmad, a dynamic force straddling the realms of academia and digital media. As a distinguished Lecturer in Information Sciences, he imparts knowledge within the academic sphere, igniting the minds of his students. Beyond the classroom, Prof. Mian Waqar Ahmad dons the hat of a seasoned blogger on Worldstan.com, where his insightful posts delve into the intricacies of information sciences. His digital footprint extends even further as a YouTuber, leveraging the platform to share his expertise and make complex concepts accessible to a global audience. Prof. Mian Waqar Ahmad’s journey embodies the fusion of traditional education and contemporary digital outreach, leaving an indelible mark on the evolving landscape of information sciences. Explore his world at Worldstan.com and witness the convergence of academia and the digital frontier.